The association between sedentary behaviour and risk of anxiety: a systematic review
- PMID: 26088005
- PMCID: PMC4474345
- DOI: 10.1186/s12889-015-1843-x
The association between sedentary behaviour and risk of anxiety: a systematic review
Abstract
Background: Previous research has linked sedentary behaviour (SB) to adverse physical health outcomes in adults and youth. Although evidence for the relationship between SB and mental health outcomes (e.g., depression) is emerging, little is known regarding risk of anxiety.
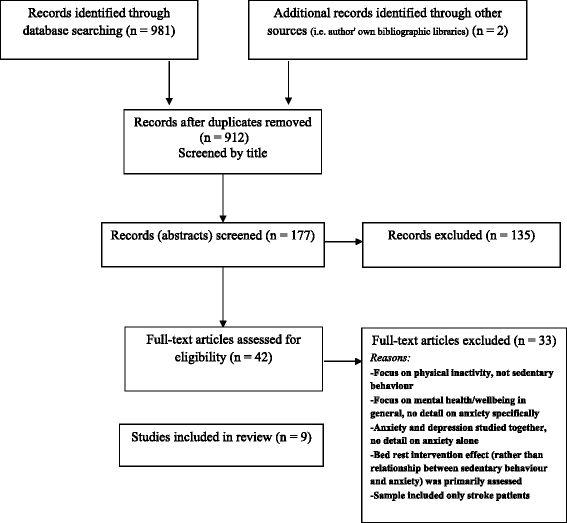
Methods: A systematic search for original research investigating the association between SB and risk of anxiety was performed using numerous electronic databases. A total of nine observational studies (seven cross-sectional and two longitudinal) were identified. Methodological quality of studies was assessed and a best-evidence synthesis was conducted.
Results: One cross-sectional study demonstrated a strong methodological quality, five cross-sectional studies demonstrated a moderate methodological quality and three studies (two cross-sectional one longitudinal) received a weak methodological quality rating. Overall, there was moderate evidence for a positive relationship between total SB and anxiety risk as well as for a positive relationship between sitting time and anxiety risk. There was inconsistent evidence for the relationship between screen time, television viewing time, computer use, and anxiety risk.
Conclusion: Limited evidence is available on the association between SB and risk of anxiety. However, our findings suggest a positive association (i.e. anxiety risk increases as SB time increases) may exist (particularly between sitting time and risk of anxiety). Further high-quality longitudinal/interventional research is needed to confirm findings and determine the direction of these relationships.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical