Genome-wide analysis, expression profile of heat shock factor gene family (CaHsfs) and characterisation of CaHsfA2 in pepper (Capsicum annuum L.)
- PMID: 26088319
- PMCID: PMC4472255
- DOI: 10.1186/s12870-015-0512-7
Genome-wide analysis, expression profile of heat shock factor gene family (CaHsfs) and characterisation of CaHsfA2 in pepper (Capsicum annuum L.)
Abstract
Background: Heat shock factors (Hsfs) play crucial roles in plant developmental and defence processes. The production and quality of pepper (Capsicum annuum L.), an economically important vegetable crop, are severely reduced by adverse environmental stress conditions, such as heat, salt and osmotic stress. Although the pepper genome has been fully sequenced, the characterization of the Hsf gene family under abiotic stress conditions remains incomplete.
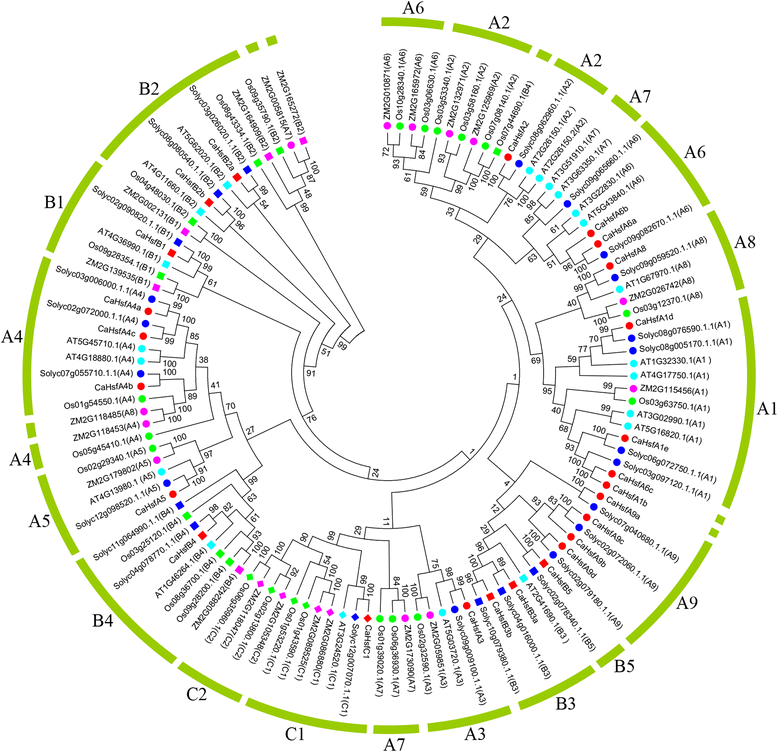
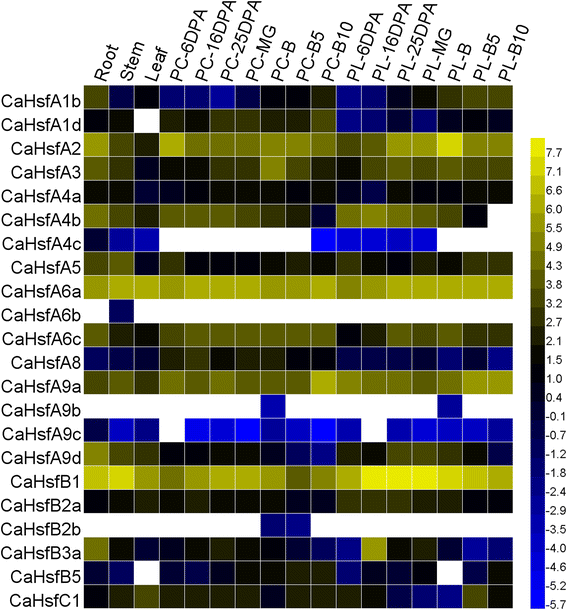
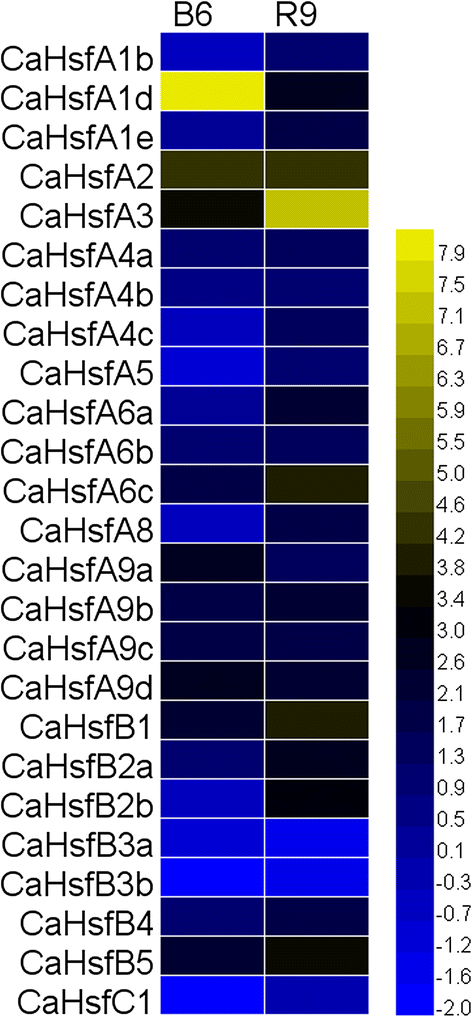
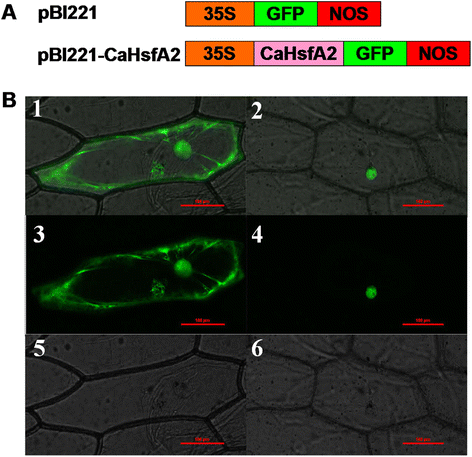
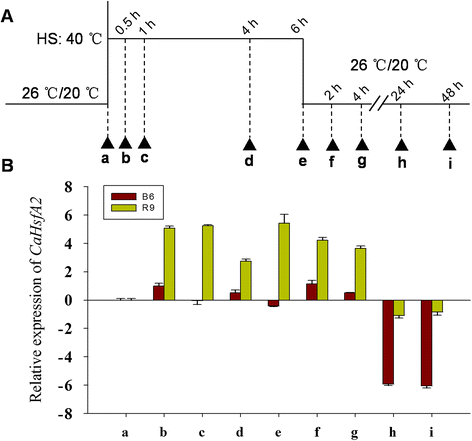
Results: A total of 25 CaHsf members were identified in the pepper genome by bioinformatics analysis and PCR assays. They were grouped into three classes, CaHsfA, B and C, based on highly conserved Hsf domains, were distributed over 11 of 12 chromosomes, with none found on chromosome 11, and all of them, except CaHsfA5, formed a protein-protein interaction network. According to the RNA-seq data of pepper cultivar CM334, most CaHsf members were expressed in at least one tissue among root, stem, leaf, pericarp and placenta. Quantitative real-time PCR assays showed that all of the CaHsfs responded to heat stress (40 °C for 2 h), except CaHsfC1 in thermotolerant line R9 leaves, and that the expression patterns were different from those in thermosensitive line B6. Many CaHsfs were also regulated by salt and osmotic stresses, as well as exogenous Ca(2+), putrescine, abscisic acid and methyl jasmonate. Additionally, CaHsfA2 was located in the nucleus and had transcriptional activity, consistent with the typical features of Hsfs. Time-course expression profiling of CaHsfA2 in response to heat stress revealed differences in its expression level and pattern between the pepper thermosensitive line B6 and thermotolerant line R9.
Conclusions: Twenty-five Hsf genes were identified in the pepper genome and most of them responded to heat, salt, osmotic stress, and exogenous substances, which provided potential clues for further analyses of CaHsfs functions in various kinds of abiotic stresses and of corresponding signal transduction pathways in pepper.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Genome-wide analysis of the Hsf family in soybean and functional identification of GmHsf-34 involvement in drought and heat stresses.BMC Genomics. 2014 Nov 21;15(1):1009. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-1009. BMC Genomics. 2014. PMID: 25416131 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide cloning, identification, classification and functional analysis of cotton heat shock transcription factors in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum).BMC Genomics. 2014 Nov 6;15(1):961. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-961. BMC Genomics. 2014. PMID: 25378022 Free PMC article.
-
Cloning and expression analysis of heat-shock transcription factor gene CaHsfA2 from pepper (Capsicum annuum L.).Genet Mol Res. 2014 Mar 17;13(1):1865-75. doi: 10.4238/2014.March.17.14. Genet Mol Res. 2014. PMID: 24668674
-
The plant heat stress transcription factor (Hsf) family: structure, function and evolution.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Feb;1819(2):104-19. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2011.10.002. Epub 2011 Oct 17. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012. PMID: 22033015 Review.
-
The SnRK2 family in pepper (Capsicum annuum L.): genome-wide identification and expression analyses during fruit development and under abiotic stress.Genes Genomics. 2020 Oct;42(10):1117-1130. doi: 10.1007/s13258-020-00968-y. Epub 2020 Jul 31. Genes Genomics. 2020. PMID: 32737808 Review.
Cited by
-
Genome-Wide Identification and Analysis of the SBP-Box Family Genes under Phytophthora capsici Stress in Pepper (Capsicum annuum L.).Front Plant Sci. 2016 Apr 15;7:504. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2016.00504. eCollection 2016. Front Plant Sci. 2016. PMID: 27148327 Free PMC article.
-
Thermo-Priming Mediated Cellular Networks for Abiotic Stress Management in Plants.Front Plant Sci. 2022 May 13;13:866409. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.866409. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35646001 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Profiling Analysis of the Xyloglucan Endotransglucosylase/Hydrolase Gene Family in Tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.).Genes (Basel). 2018 May 24;9(6):273. doi: 10.3390/genes9060273. Genes (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29795009 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic regions associated with physiological, biochemical and yield-related responses under water deficit in diploid potato at the tuber initiation stage revealed by GWAS.PLoS One. 2021 Nov 8;16(11):e0259690. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0259690. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34748612 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome based identification and validation of heat stress transcription factors in wheat progenitor species Aegilops speltoides.Sci Rep. 2021 Nov 11;11(1):22049. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-01596-6. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34764387 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wardlaw IF, Wrigley CW. Heat tolerance in temperate cereals: an overview. Aust J Plant Physiol. 1994;21(6):695–703. doi: 10.1071/PP9940695. - DOI
-
- Skylas DJ, Cordwell SJ, Hains PG, Larsen MR, Basseal DJ, Walsh BJ, et al. Heat shock of wheat during grain filing: proteins associated with heat-tolerance. J Cereal Sci. 2002;35(2):175–188. doi: 10.1006/jcrs.2001.0410. - DOI
-
- Bar-Tsur A, Rudich J, Bravdo B. High temperature effects on CO2 gas exchange in heat-tolerant and sensitive tomatoes. J Am Soc Hort Sci. 1985;110:582–586.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

