A Transparent Window into Biology: A Primer on Caenorhabditis elegans
- PMID: 26088431
- PMCID: PMC4492366
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.115.176099
A Transparent Window into Biology: A Primer on Caenorhabditis elegans
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum.Genetics. 2015 Sep;201(1):339. doi: 10.1534/genetics.115.180133. Genetics. 2015. PMID: 26354977 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
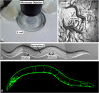
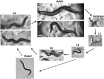
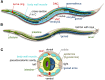
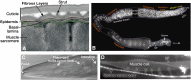
A little over 50 years ago, Sydney Brenner had the foresight to develop the nematode (round worm) Caenorhabditis elegans as a genetic model for understanding questions of developmental biology and neurobiology. Over time, research on C. elegans has expanded to explore a wealth of diverse areas in modern biology including studies of the basic functions and interactions of eukaryotic cells, host-parasite interactions, and evolution. C. elegans has also become an important organism in which to study processes that go awry in human diseases. This primer introduces the organism and the many features that make it an outstanding experimental system, including its small size, rapid life cycle, transparency, and well-annotated genome. We survey the basic anatomical features, common technical approaches, and important discoveries in C. elegans research. Key to studying C. elegans has been the ability to address biological problems genetically, using both forward and reverse genetics, both at the level of the entire organism and at the level of the single, identified cell. These possibilities make C. elegans useful not only in research laboratories, but also in the classroom where it can be used to excite students who actually can see what is happening inside live cells and tissues.
Keywords: C. elegans; Primer; nematodes; single-cell analysis; transparent genetic system.
Copyright © 2015 Corsi, Wightman, and Chalfie.
Figures


References
-
- Ahringer, J., 2006 Reverse genetics (April 6, 2006), WormBook, ed. The C. elegans Research Community, WormBook, /10.1895/wormbook.1.47.1, http://www.wormbook.org.
-
- Albertson D. G., and J. N. Thomson, 1976 The pharynx of Caenorhabditis elegans. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 275:299–325. - PubMed
-
- Altun Z. F., Herndon L. A., Crocker C., Lints R., Hall D. H. (eds), 2002–2015. WormAtlas. Available at: http://www.wormatlas.org.
-
- Ambros V., Horvitz H. R., 1984. Heterochronic mutants of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Science 226: 409–416. - PubMed
-
- Ardiel E. L., Rankin C. H., 2010. An elegant mind: learning and memory in Caenorhabditis elegans. Learn. Mem. 17: 191–201. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

