Emerging clinical applications of computed tomography
- PMID: 26089707
- PMCID: PMC4467659
- DOI: 10.2147/MDER.S70630
Emerging clinical applications of computed tomography
Abstract
X-ray computed tomography (CT) has recently been experiencing remarkable growth as a result of technological advances and new clinical applications. This paper reviews the essential physics of X-ray CT and its major components. Also reviewed are recent promising applications of CT, ie, CT-guided procedures, CT-based thermometry, photon-counting technology, hybrid PET-CT, use of ultrafast-high pitch scanners, and potential use of dual-energy CT for material differentiations. These promising solutions and a better knowledge of their potentialities should allow CT to be used in a safe and effective manner in several clinical applications.
Keywords: X-ray; computed tomography; dual-energy; guidance; photon-counting technology; thermometry; ultrafast scanner.
Figures
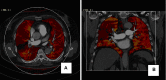
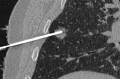

References
-
- Cormack AM. Reconstruction of densities from their projections, with applications in radiological physics. Phys Med Biol. 1973;18:195–207. - PubMed
-
- Hounsfield GN. Computerized transverse axial scanning (tomography) part 1. Description of the system. Br J Radiol. 1973;46:1016–1022. - PubMed
-
- Cierniak R. X-Ray Computed Tomography in Biomedical Engineering. London, UK: Springer-Verlag; 2011.
-
- Röntgen WC. Über eine neue Art von Strahlen. Sitzungsberichte der Physikalisch-medizinischen Gesellschaft zu Würzburg [on a new kind of rays] Science. 1896;3:227–231. German. - PubMed
-
- Thomson E. Stereoscopic roentgen pictures. Electr Eng. 1896;21:256.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

