Teaching signal detection theory with pseudoscience
- PMID: 26089813
- PMCID: PMC4452803
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2015.00762
Teaching signal detection theory with pseudoscience
Keywords: decision-making; pedagogy; pseudoscience; scientific thinking; signal detection.
Figures
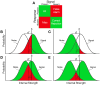
References
-
- Banks W. P. (1970). Signal detection theory and human memory. Psychol. Bull. 74, 81–99.
-
- Fisher C. R. (2014). Using spreadsheets to teach signal detection theory. Spreadsheets Educ. (eJSiE) 7, 1–18. Available online at: http://epublications.bond.edu.au/ejsie/ - PubMed
-
- Garfield J., Ben-Zvi B. (2007). How students learn statistics revisited: a current review of research on teaching and learning statistics. Int. Stat. Rev. 75, 372–396. 10.1111/j.1751-5823.2007.00029.x - DOI
-
- Goldstein E. B. (2014). Sensation and Perception, 9th Edn. Belmont, CA: Wadsworth.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

