The Protective Effect of Resveratrol on Concanavalin-A-Induced Acute Hepatic Injury in Mice
- PMID: 26089871
- PMCID: PMC4458299
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/506390
The Protective Effect of Resveratrol on Concanavalin-A-Induced Acute Hepatic Injury in Mice
Abstract
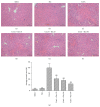
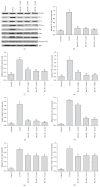
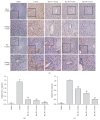
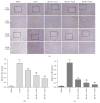
Pharmacologic Relevance. Resveratrol, an antioxidant derived from grapes, has been reported to modulate the inflammatory process. In this study, we investigated the effects of resveratrol and its mechanism of protection on concanavalin-A- (ConA-) induced liver injury in mice. Materials and Methods. Acute autoimmune hepatitis was induced by ConA (20 mg/kg) in Balb/C mice; mice were treated with resveratrol (10, 20, and 30 mg/kg) daily by oral gavage for fourteen days prior to a single intravenous injection of ConA. Eight hours after injection, histologic grading, proinflammatory cytokine levels, and hedgehog pathway activity were determined. Results. After ConA injection, the cytokines IL-2, IL-6, and TNF-α were increased, and Sonic hedgehog (Shh), Glioblastoma- (Gli-) 1, and Patched (Ptc) levels significantly increased. Pretreatment with resveratrol ameliorated the pathologic effects of ConA-induced autoimmune hepatitis and significantly inhibited IL-2, IL-6, TNF-α, Shh, Gli-1, and Ptc. The effects of resveratrol on the hedgehog pathway were studied by western blotting and immunohistochemistry. Resveratrol decreased Shh expression, possibly by inhibiting Shh expression in order to reduce Gli-1 and Ptc expression. Conclusion. Resveratrol protects against ConA-induced autoimmune hepatitis by decreasing cytokines expression in mice. The decreases seen in Gli-1 and Ptc may correlate with the amelioration of hedgehog pathway activity.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Protective effects of a traditional Chinese herbal formula Jiang-Xian HuGan on Concanavalin A-induced mouse hepatitis via NF-κB and Nrf2 signaling pathways.J Ethnopharmacol. 2018 May 10;217:118-125. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2018.02.003. Epub 2018 Feb 5. J Ethnopharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29421593
-
Resveratrol Activated Sonic Hedgehog Signaling to Enhance Viability of NIH3T3 Cells in Vitro via Regulation of Sirt1.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;50(4):1346-1360. doi: 10.1159/000494593. Epub 2018 Oct 24. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 30355933
-
Ethyl pyruvate pretreatment attenuates concanavalin a-induced autoimmune hepatitis in mice.PLoS One. 2014 Feb 3;9(2):e87977. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0087977. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24498418 Free PMC article.
-
Shikonin Attenuates Concanavalin A-Induced Acute Liver Injury in Mice via Inhibition of the JNK Pathway.Mediators Inflamm. 2016;2016:2748367. doi: 10.1155/2016/2748367. Epub 2016 May 16. Mediators Inflamm. 2016. PMID: 27293314 Free PMC article.
-
Resveratrol Enhances Neurite Outgrowth and Synaptogenesis Via Sonic Hedgehog Signaling Following Oxygen-Glucose Deprivation/Reoxygenation Injury.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;43(2):852-869. doi: 10.1159/000481611. Epub 2017 Sep 28. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28957797
Cited by
-
Salidroside mediates apoptosis and autophagy inhibition in concanavalin A-induced liver injury.Exp Ther Med. 2018 Jun;15(6):4599-4614. doi: 10.3892/etm.2018.6053. Epub 2018 Apr 12. Exp Ther Med. 2018. PMID: 29805476 Free PMC article.
-
Summary of Natural Products Ameliorate Concanavalin A-Induced Liver Injury: Structures, Sources, Pharmacological Effects, and Mechanisms of Action.Plants (Basel). 2021 Jan 25;10(2):228. doi: 10.3390/plants10020228. Plants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33503905 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatoprotective Effect of Camel Thorn Polyphenols in Concanavalin A-Induced Hepatitis in Mice.Chin J Integr Med. 2024 Dec;30(12):1090-1100. doi: 10.1007/s11655-024-3808-3. Epub 2024 Sep 19. Chin J Integr Med. 2024. PMID: 39298072
-
Expression of scavenger receptor A in rat's liver tissue during acute obstructive cholangitis and its significance.Springerplus. 2016 May 12;5:606. doi: 10.1186/s40064-016-2222-5. eCollection 2016. Springerplus. 2016. PMID: 27247902 Free PMC article.
-
Coadjuvants in the Diabetic Complications: Nutraceuticals and Drugs with Pleiotropic Effects.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Aug 5;17(8):1273. doi: 10.3390/ijms17081273. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27527163 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Heron M., Hoyert D. L., Murphy S. L., et al. Deaths: Final Data for 2006. Hyattsville, Md, USA: National Center for Health Statistics; 2009. (National Vital Statistics Report). - PubMed
-
- American Gastroenterological Association. The Burden of Gastrointestinal Diseases. Bethesda, Md, USA: American Gastroenterological Diseases, American Gastroenterological Association; 2001.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

