Readmission destination and risk of mortality after major surgery: an observational cohort study
- PMID: 26093917
- PMCID: PMC4851558
- DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)60087-3
Readmission destination and risk of mortality after major surgery: an observational cohort study
Abstract
Background: Hospital readmissions are common after major surgery, although it is unknown whether patients achieve improved outcomes when they are readmitted to, and receive care at, the index hospital where their surgical procedure was done. We examined the association between readmission destination and mortality risk in the USA in Medicare beneficiaries after a range of common operations.
Methods: By use of claims data from Medicare beneficiaries in the USA between Jan 1, 2001, and Nov 15, 2011, we assessed patients who needed hospital readmission within 30 days after open abdominal aortic aneurysm repair, infrainguinal arterial bypass, aortobifemoral bypass, coronary artery bypass surgery, oesophagectomy, colectomy, pancreatectomy, cholecystectomy, ventral hernia repair, craniotomy, hip replacement, or knee replacement. We used logistic regression models incorporating inverse probability weighting and instrumental variable analysis to measure associations between readmission destination (index vs non-index hospital) and risk of 90 day mortality for patients who underwent surgery who needed hospital readmission.
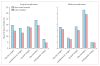
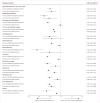
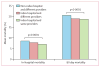
Findings: 9,440,503 patients underwent one of 12 major operations, and the number of patients readmitted or transferred back to the index hospital where their operation was done varied from 186,336 (65·8%) of 283,131 patients who were readmitted after coronary artery bypass grafting, to 142,142 (83·2%) of 170,789 patients who were readmitted after colectomy. Readmission was more likely to be to the index hospital than to a non-index hospital if the readmission was for a surgical complication (189,384 [23%] of 834,070 patients readmitted to index hospital vs 36,792 [13%] of 276,976 patients readmitted non-index hospital, p<0·0001). Readmission to the index hospital was associated with a 26% lower risk of 90 day mortality than was readmission to a non-index hospital, with inverse probability weighting used to control for selection bias (odds ratio [OR] 0·74, 95% CI 0·66-0·83). This effect was significant (p<0·0001) for all procedures in inverse probability-weighted models, and was largest for patients who were readmitted after pancreatectomy (OR 0·56, 95% CI 0·45-0·69) and aortobifemoral bypass (OR 0·69, 95% CI 0·61-0·77). By use of hospital-level variation among regional index hospital readmission rates as an instrument, instrumental variable analysis showed that the patients with the highest probability of returning to the index hospital had 8% lower risk of mortality (OR 0·92 95% CI 0·91-0·94) than did patients who were less likely to be readmitted to the index hospital.
Interpretation: In the USA, patients who are readmitted to hospital after various major operations consistently achieve improved survival if they return to the hospital where their surgery took place. These findings might have important implications for cost-effectiveness-driven regional centralisation of surgical care.
Funding: None.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare no competing interests.
Figures
Comment in
-
Hospital readmission after surgery: no place like home.Lancet. 2015 Aug 29;386(9996):837-9. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)60462-7. Epub 2015 Jun 17. Lancet. 2015. PMID: 26093916 No abstract available.
-
Improved Outcomes When Surgical Postoperative Complications Are Managed According to the Principles of Continuity of Care and Specificity of Expertise.J Patient Saf. 2019 Dec;15(4):e15-e16. doi: 10.1097/PTS.0000000000000302. J Patient Saf. 2019. PMID: 28846553 No abstract available.
References
-
- Birkmeyer JD, Dimick JB, Birkmeyer NJ. Measuring the quality of surgical care: structure, process, or outcomes? J Am Coll Surg. 2004;198:626–32. - PubMed
-
- Ingraham AM, Richards KE, Hall BL, Ko CY. Quality improvement in surgery: the American College of Surgeons National Surgical Quality Improvement Program approach. Adv Surg. 2010;44:251–67. - PubMed
-
- Luft HS, Bunker JP, Enthoven AC. Should operations be regionalized? The empirical relation between surgical volume and mortality. N Engl J Med. 1979;301:1364–69. - PubMed
-
- Hollenbeck BK, Miller DC, Wei JT, Montie JE. Regionalization of care: centralizing complex surgical procedures. Nat Clin Pract Urol. 2005;2:461. - PubMed
-
- Ghaferi AA, Birkmeyer JD, Dimick JB. Variation in hospital mortality associated with inpatient surgery. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:1368–75. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

