A Review of Inflammatory Processes of the Breast with a Focus on Diagnosis in Core Biopsy Samples
- PMID: 26095437
- PMCID: PMC4508565
- DOI: 10.4132/jptm.2015.06.11
A Review of Inflammatory Processes of the Breast with a Focus on Diagnosis in Core Biopsy Samples
Abstract
Inflammatory and reactive lesions of the breast are relatively uncommon among benign breast lesions and can be the source of an abnormality on imaging. Such lesions can simulate a malignant process, based on both clinical and radiographic findings, and core biopsy is often performed to rule out malignancy. Furthermore, some inflammatory processes can mimic carcinoma or other malignancy microscopically, and vice versa. Diagnostic difficulty may arise due to the small and fragmented sample of a core biopsy. This review will focus on the pertinent clinical, radiographic, and histopathologic features of the more commonly encountered inflammatory lesions of the breast that can be characterized in a core biopsy sample. These include fat necrosis, mammary duct ectasia, granulomatous lobular mastitis, diabetic mastopathy, and abscess. The microscopic differential diagnoses for these lesions when seen in a core biopsy sample will be discussed.
Keywords: Breast; Core biopsy; Inflammatory; Mammogram.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
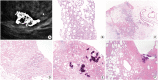
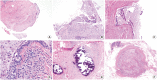
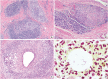
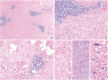
References
-
- Clarke D, Curtis JL, Martinez A, Fajardo L, Goffinet D. Fat necrosis of the breast simulating recurrent carcinoma after primary radiotherapy in the management of early stage breast carcinoma. Cancer. 1983;52:442–5. - PubMed
-
- Shah C, Badiyan S, Ben Wilkinson J, et al. Treatment efficacy with accelerated partial breast irradiation (APBI): final analysis of the American Society of Breast Surgeons MammoSite((R)) breast brachytherapy registry trial. Ann Surg Oncol. 2013;20:3279–85. - PubMed
-
- Aqel NM, Howard A, Collier DS. Fat necrosis of the breast: a cytological and clinical study. Breast. 2001;10:342–5. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

