FISH and array CGH characterization of de novo derivative Y chromosome (Yq duplication and partial Yp deletion) in an azoospermic male
- PMID: 26096031
- PMCID: PMC4758203
- DOI: 10.1016/j.rbmo.2015.04.014
FISH and array CGH characterization of de novo derivative Y chromosome (Yq duplication and partial Yp deletion) in an azoospermic male
Abstract
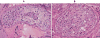
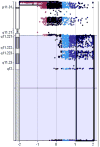
This study presents a 28-year-old infertile male who was referred to the cytogenetic laboratory for chromosomal analysis after 4 years of regular unprotected intercourse in whom non-obstructive azoospermia was revealed. Standard cytogenetic G-banding was performed on metaphase spreads and a de-novo karyotype 46,X,der(Y)(q11.22;p11.3) was identified. This analysis was followed by flourescence in-situ hybridization(FISH) and array comparative genomic hybridization (aCGH). Finally, the patient's karyotype was identified as 46,X,der(Y)(qter→q11.221::p11.31→qter).ish der(Y) (qter+,pter-,SHOX+,SRY+,Ycen+,DYZ3+;DYZ1+,qter+).arrYq11.221q12(14,448,863-59,288,511) x2, Yp11.32p11.31(104,062-266,388) x0. It is proposed that de-novo derivative monocentric Y chromosome with duplicated region Y qter→q11.221::p11.31→qter with partial deletion of Yp PAR1 region most probably can perturb the conjugation of sex chromosomes during first meiotic division of spermatogenic arrested differentiation (development).
Keywords: FISH; aCGH; azoospermia; der(Y); intrachromosomal duplication and translocation; pseudoisomonocentric.
Copyright © 2015 Reproductive Healthcare Ltd. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration: The author reports no financial or commercial conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Duplication of Yq- and proximal Yp-arms with deletion of almost all PAR1 (including SHOX) in a young man with non-obstructive azoospermia, short stature and skeletal defects.J Appl Genet. 2017 Nov;58(4):481-486. doi: 10.1007/s13353-017-0412-7. Epub 2017 Oct 6. J Appl Genet. 2017. PMID: 29019057
-
Array-CGH characterization of a prenatally detected de novo 46,X,der(Y)t(X;Y)(p22.3;q11.2) in a male fetus.Eur J Med Genet. 2011 May-Jun;54(3):333-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmg.2011.02.003. Epub 2011 Feb 24. Eur J Med Genet. 2011. PMID: 21354345
-
Molecular cytogenetic characterization of an isodicentric Yq and a neocentric isochromosome Yp in an azoospermic male.Mol Med Rep. 2020 Feb;21(2):918-926. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2019.10883. Epub 2019 Dec 13. Mol Med Rep. 2020. PMID: 31974623
-
Delineating the association between isodicentric chromosome Y and infertility: a retrospective study.Fertil Steril. 2014 Apr;101(4):1091-6. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2013.12.048. Epub 2014 Feb 4. Fertil Steril. 2014. PMID: 24502892 Review.
-
Perinatal findings and molecular cytogenetic analysis of de novo partial trisomy 16q (16q22.1-->qter) and partial monosomy 20q (20q13.3-->qter).Prenat Diagn. 2005 Feb;25(2):112-8. doi: 10.1002/pd.1083. Prenat Diagn. 2005. PMID: 15712324 Review.
Cited by
-
Duplication of Yq- and proximal Yp-arms with deletion of almost all PAR1 (including SHOX) in a young man with non-obstructive azoospermia, short stature and skeletal defects.J Appl Genet. 2017 Nov;58(4):481-486. doi: 10.1007/s13353-017-0412-7. Epub 2017 Oct 6. J Appl Genet. 2017. PMID: 29019057
-
A de novo derivative Y chromosome (partial Yq deletion and partial duplication of Yp and Yq) in a female with disorders of sex development.Clin Case Rep. 2018 Jul 7;6(9):1671-1676. doi: 10.1002/ccr3.1613. eCollection 2018 Sep. Clin Case Rep. 2018. PMID: 30214739 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic testing for copy number and single nucleotide variants in spermatogenic failure.J Assist Reprod Genet. 2022 Sep;39(9):2103-2114. doi: 10.1007/s10815-022-02538-5. Epub 2022 Jul 18. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2022. PMID: 35849255 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alves C, Carvalho F, Cremades N, Sousa M, Barros A. Unique (Y;13) translocation in a male with oligozoospermia: cytogenetic and molecular studies. Eur J Hum Genet. 2002;10:467–474. - PubMed
-
- Bernasconi S, Garavelli L. A short history of the initial discovery of the SHOX gene. J Endocrinol Invest. 2010;33(6 Suppl):3–6. - PubMed
-
- Brisset S, Izard V, Misrahi M, Aboura A, Madoux S, Ferlicot S, Schoevaert D, Soufir JC, Frydman R, Tachdjian G. Cytogenetic, molecular and testicular tissue studies in an infertile 45,X male carrying an unbalanced (y;22) translocation: case report. Hum Reprod. 2005;20:2168–2172. - PubMed
-
- Bukvic N, Cesarano C, Ceccarini C, Bruno M, Lipsi RM, Gallicchio GM, Carboni AM, Valente L, Cotoia G, Antonetti R. Characterization of the first adult de novo case of 46,X,der(Y)t(X;Y)(p22.3;q11.2) Gene. 2013;513:111–117. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

