Eubacteria and archaea communities in seven mesophile anaerobic digester plants in Germany
- PMID: 26097504
- PMCID: PMC4474353
- DOI: 10.1186/s13068-015-0271-6
Eubacteria and archaea communities in seven mesophile anaerobic digester plants in Germany
Abstract
Background: Only a fraction of the microbial species used for anaerobic digestion in biogas production plants are methanogenic archaea. We have analyzed the taxonomic profiles of eubacteria and archaea, a set of chemical key parameters, and biogas production in samples from nine production plants in seven facilities in Thuringia, Germany, including co-digesters, leach-bed, and sewage sludge treatment plants. Reactors were sampled twice, at a 1-week interval, and three biological replicates were taken in each case.
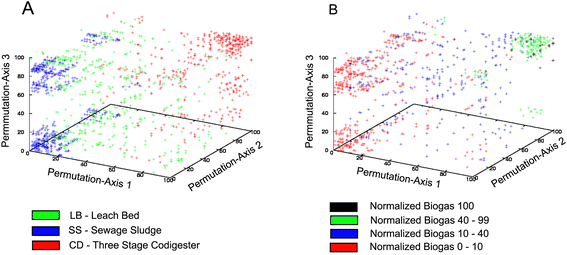
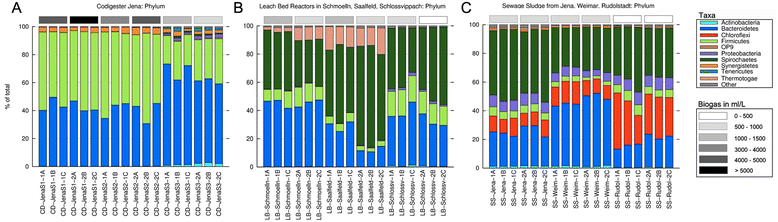
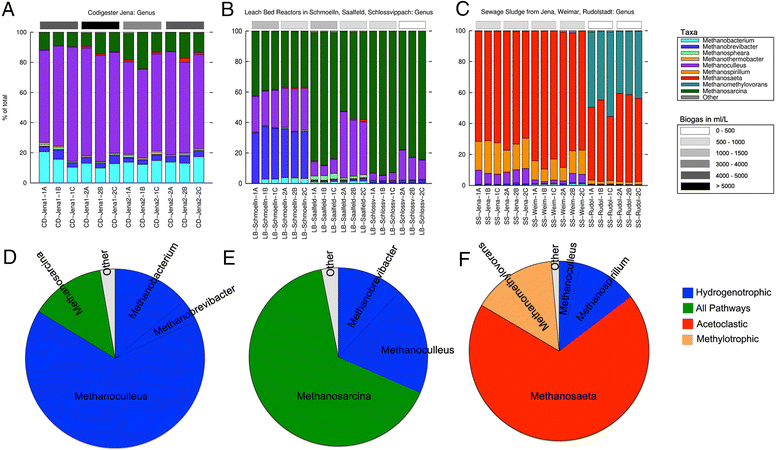
Results: A complex taxonomic composition was found for both eubacteria and archaea, both of which strongly correlated with digester type. Plant-degrading Firmicutes as well as Bacteroidetes dominated eubacteria profiles in high biogas-producing co-digesters; whereas Bacteroidetes and Spirochaetes were the major phyla in leach-bed and sewage sludge digesters. Methanoculleus was the dominant archaea genus in co-digesters, whereas Methanosarcina and Methanosaeta were the most abundant methanogens in leachate from leach-bed and sewage sludge digesters, respectively.
Conclusions: This is one of the most comprehensive characterizations of the microbial communities of biogas-producing facilities. Bacterial profiles exhibited very low variation within replicates, including those of semi-solid samples; and, in general, low variation in time. However, facility type correlated closely with the bacterial profile: each of the three reactor types exhibited a characteristic eubacteria and archaea profile. Digesters operated with solid feedstock, and high biogas production correlated with abundance of plant degraders (Firmicutes) and biofilm-forming methanogens (Methanoculleus spp.). By contrast, low biogas-producing sewage sludge treatment digesters correlated with high titers of volatile fatty acid-adapted Methanosaeta spp.
Keywords: Anaerobic digesters; Archaea; Biogas; Eubacteria; Methanogens.
Figures
References
-
- Bagley JE, Miller J, Bernacchi CJ. Biophysical impacts of climate-smart agriculture in the midwest United States. Plant Cell Environ. 2014 - PubMed
-
- Scoma A, Rebecchi S, Bertin L, Fava F. High impact biowastes from South European agro-industries as feedstock for second-generation biorefineries. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2014;1–15. - PubMed
-
- European Commission . Renewable energy road map renewable energies in the 21st century: building a more sustainable future. KOM (2006) 848 final. Brussels: European Commission; 2007.
-
- Eurostat—database, source code ten00081 and ten00082. Primary production of renewable energy, 2000 and 2010. [http://epp.eurostat.ec.europa.eu/statistics_explained/index.php/File:Pri...]
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

