Possible antiosteoporotic mechanism of Cicer arietinum extract in ovariectomized rats
- PMID: 26097532
- PMCID: PMC4466919
Possible antiosteoporotic mechanism of Cicer arietinum extract in ovariectomized rats
Abstract
Objective: The present study aimed to throw the light on the anti-osteoprotic mechanism of Cicer arietinum extract (CAE) seeds against ovariectomized (OVX) rats.
Methods: Seventy female rats were divided into two groups. The first group (14 rats/group) represented normal rats (Sham operated) while the second group (56 rats/group) underwent bilateral ovariectomy (OVX). After one week of recovery from ovariectomy surgery, the second group was randomly subdivided into 4 subgroups (14 rats/ each subgroup). The rats administered orally; distilled water (vehicle) (1st subgroup), Cicer arietinum extract (CAE) (500 or 1000 mg/kg body weight/day) (2nd and 3rd subgroups), alendronate (6.5 mg/kg mg/kg body weight) as a positive control one time/week (4(rh) subgroup), daily for 10 weeks.
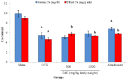
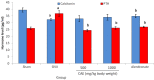
Results: The present study demonstrated that ovariectomy caused significant decrease in bone mineral; density (BMD) and content (BMC), Bone-specific alkaline phosphatase (BALP), calcium (Ca), phosphorus (P), parathyroid hormone (PTH) and calcitonin levels. Furthermore, ovariectomy induced significant elevation of tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase 5b (TRAP 5b) and receptor activator of nuclear factor (NF-kappa β) ligand (RANKL) concentration. Conversely, osteoprotegerin (OPG) and OPG/RANKL ratio were decreased following ovariectomy. The present work suggests that CAE has antiosteoporotic action against ovariectomy effects and its activity may results from its phytochemical and/or phytoestrogen contents.
Conclusion: The ongoing study speculates that the CAE exerts its action through regulation of RANK/RANKL/OPG system. As, CAE not only promotes osteoblast differentiation, but also up-regulates OPG and downregulates RANKL secretion in osteoblasts, subsequently prevents bone loss and osteoporosis.
Keywords: Cicer arietinum; bone remodeling regulators; bone resorption marker; osteoporosis; ovariectomy.
Figures
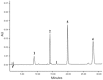
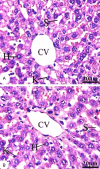
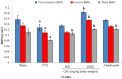
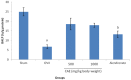

References
-
- Deyhim F, Garica K, Lopez E, Gonzalez J, Ino S, Garcia M, Patil BS. Citrus juice modulates bone strength in male senescent rat model of osteoporosis. Nutrition. 2006;22:559–563. - PubMed
-
- Kim YH, Kim GS, Jeong-Hwa B. Inhibitory action of bisphosphonates on bone resorption does not involve the regulation of RANKL and OPG expression. Exp Mol Med. 2002;34:145–151. - PubMed
-
- Hanan SA, Sahar YM. Perceived self-efficacy and commitment to an exercise in patients with osteoporosis and osteoarthritis. J Am Sci. 2011;7:315–323.
-
- Cashman KD. Diet, nutrition and bone health. J Nutr. 2007;137:2507s–2512s. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
