Comparative efficacy of methylphenidate and atomoxetine in oppositional defiant disorder comorbid with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder
- PMID: 26097819
- PMCID: PMC4456885
- DOI: 10.4103/2229-516X.157162
Comparative efficacy of methylphenidate and atomoxetine in oppositional defiant disorder comorbid with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder
Abstract
Background: Oppositional defiant disorder (ODD) is frequently comorbid with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and is associated with substantial functional impairments. Methylphenidate and atomoxetine are well-established drugs for the management of ADHD. Some studies from Western countries have reported these drugs to be effective in the management of ODD comorbid with ADHD. This study aimed to assess if methylphenidate and atomoxetine are efficacious in treating Indian children with ODD comorbid with ADHD.
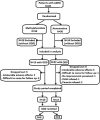
Subjects and methods: In this prospective, open-label study, 37 patients of age 6-14 years with a diagnosis of ODD comorbid with ADHD randomly received either methylphenidate (dose 0.2-1 mg/kg/day) or atomoxetine (dose 0.5-1.2 mg/kg/day) for 8 weeks. Improvements in ADHD and ODD symptoms were assessed using Vanderbilt ADHD diagnostic parent rating scale (VADPRS).
Results: At 8 weeks, there were statistically significant improvements in both ADHD and ODD symptoms in both methylphenidate and atomoxetine groups, as per VADPRS. The improvements produced and tolerability was comparable in the two groups. 80% of the patients from methylphenidate group and 64.3% patients from atomoxetine group ceased to fulfill the criteria for the presence of ODD at 8 weeks.
Conclusions: Methylphenidate and atomoxetine are effective in the treatment of ODD comorbid with ADHD in short duration.
Keywords: Atomoxetine; attention deficit hyperactivity disorder; methylphenidate; oppositional defiant disorder.
Conflict of interest statement
References
-
- Text Revision. 4th ed. Washington DC: American Psychiatric Association; 2000. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorder.
-
- Turgay A. Psychopharmacological treatment of oppositional defiant disorder. CNS Drugs. 2009;23:1–17. - PubMed
-
- Hamilton SS, Armando J. Oppositional defiant disorder. Am Fam Physician. 2008;78:861–6. - PubMed
-
- Rader R, McCauley L, Callen EC. Current strategies in the diagnosis and treatment of childhood attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Am Fam Physician. 2009;79:657–65. - PubMed
-
- Kuhne M, Schachar R, Tannock R. Impact of comorbid oppositional or conduct problems on attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 1997;36:1715–25. - PubMed