[Pathologic aerophagia: a rare cause of chronic abdominal distension]
- PMID: 26100594
- PMCID: PMC4620966
- DOI: 10.1016/j.rpped.2015.01.003
[Pathologic aerophagia: a rare cause of chronic abdominal distension]
Abstract
Objective:: To describe an adolescent with pathologic aerophagia, a rare condition caused by excessive and inappropriate swallowing of air and to review its treatment and differential diagnoses.
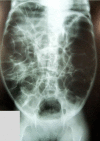
Case description:: An 11-year-old mentally impaired blind girl presenting serious behavior problems and severe developmental delay with abdominal distension from the last 8 months. Her past history included a Nissen fundoplication. Abdominal CT and abdominal radiographs showed diffuse gas distension of the small bowel and colon. Hirschsprung's disease was excluded. The distention was minimal at the moment the child awoke and maximal at evening, and persisted after control of constipation. Audible repetitive and frequent movements of air swallowing were observed. The diagnosis of pathologic aerophagia associated to obsessive-compulsive disorder and developmental delay was made, but pharmacological treatment was unsuccessful. The patient was submitted to an endoscopic gastrostomy, permanently opened and elevated relative to the stomach. The distention was resolved, while maintaining oral nutrition.
Comments:: Pathologic aerophagia is a rare self-limiting condition in normal children exposed to high levels of stress and may be a persisting problem in children with psychiatric or neurologic disease. In this last group, the disease may cause serious complications. Pharmacological and behavioral treatments are ill-defined. Severe cases may demand surgical strategies, mainly decompressive gastrostomy.
Keywords: Aerofagia; Aerophagy; Distensão patológica; Esvaziamento gástrico; Gastric emptying; Pathologic dilatation.
Copyright © 2015 Sociedade de Pediatria de São Paulo. Publicado por Elsevier Editora Ltda. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Colon perforation due to pathologic aerophagia in an intellectually disabled child.J Paediatr Child Health. 2007 Oct;43(10):710-2. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1754.2007.01190.x. J Paediatr Child Health. 2007. PMID: 17854458
-
Clinical features of pathologic childhood aerophagia: early recognition and essential diagnostic criteria.J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2005 Nov;41(5):612-6. doi: 10.1097/01.mpg.0000179856.68968.e0. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2005. PMID: 16254518
-
Observational study of children with aerophagia.Clin Pediatr (Phila). 2008 Sep;47(7):664-9. doi: 10.1177/0009922808315825. Epub 2008 Apr 29. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 2008. PMID: 18445758
-
Physiologic and pathologic belching.Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007 Jul;5(7):772-5. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2007.02.018. Epub 2007 May 4. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007. PMID: 17481963 Review.
-
Management of belching, hiccups, and aerophagia.Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013 Jan;11(1):6-12. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2012.09.006. Epub 2012 Sep 13. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013. PMID: 22982101 Review.
Cited by
-
Gastric Necrosis and Perforation Following Massive Gastric Dilatation in an Adolescent Girl: A Rare Cause of Acute Abdomen.Front Surg. 2019 Jan 30;6:3. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2019.00003. eCollection 2019. Front Surg. 2019. PMID: 30761307 Free PMC article.
-
[Clinical features and etiology of abdominal distension in children].Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2019 Oct;21(10):1022-1027. doi: 10.7499/j.issn.1008-8830.2019.10.013. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 31642438 Free PMC article. Chinese.
References
-
- Loening-Baucke V. Aerophagia as cause of gaseous abdominal distension in a toddler. J Pediatr Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2000;31:204–207. - PubMed
-
- Fukuzawa H, Urushihara N, Fukumoto K, Sugiyama A, Mitsunaga M, Watanabe K, et al. Esophagogastric separation and abdominal esophagostomy via jejunal interposition: a new operation for extreme forms of pathologic aerophagia. J Pediatr Surg. 2011;46:2035–2037. - PubMed
-
- Lecine T, Michaud L, Gottrand F, Launay V, Faure C, Bonnevalle M, et al. Children who swallow air. Arch Pediatr. 1998;5:1224–1228. - PubMed
-
- Hwang JB, Choi WJ, Kim JS, Lee SY, Jung CH, Lee YH, et al. Clinical features of pathologic childhood aerophagia: early recognition and essential diagnostic criteria. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2005;41:612–616. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

