Novel Allosteric Modulators of G Protein-coupled Receptors
- PMID: 26100627
- PMCID: PMC4528113
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.R115.662759
Novel Allosteric Modulators of G Protein-coupled Receptors
Abstract
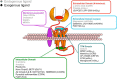
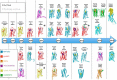
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) are allosteric proteins, because their signal transduction relies on interactions between topographically distinct, yet conformationally linked, domains. Much of the focus on GPCR allostery in the new millennium, however, has been on modes of targeting GPCR allosteric sites with chemical probes due to the potential for novel therapeutics. It is now apparent that some GPCRs possess more than one targetable allosteric site, in addition to a growing list of putative endogenous modulators. Advances in structural biology are also shedding new insights into mechanisms of allostery, although the complexities of candidate allosteric drugs necessitate rigorous biological characterization.
Keywords: G protein; G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR); allosteric regulation; biased agonism; bitopic ligand; chemical biology; drug discovery; structural biology.
© 2015 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Fredriksson R., Lagerström M. C., Lundin L.-G., Schiöth H. B. (2003) The G-protein-coupled receptors in the human genome form five main families: phylogenetic analysis, paralogon groups, and fingerprints. Mol. Pharmacol. 63, 1256–1272 - PubMed
-
- Oldham W. M., Hamm H. E. (2006) Structural basis of function in heterotrimeric G proteins. Q. Rev. Biophys. 39, 117–166 - PubMed
-
- Rask-Andersen M., Almén M. S., Schiöth H. B. (2011) Trends in the exploitation of novel drug targets. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 10, 579–590 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

