Diallyl disulfide inhibits TNFα induced CCL2 release through MAPK/ERK and NF-Kappa-B signaling
- PMID: 26100848
- PMCID: PMC4532635
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cyto.2014.12.007
Diallyl disulfide inhibits TNFα induced CCL2 release through MAPK/ERK and NF-Kappa-B signaling
Abstract
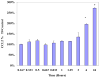
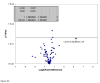
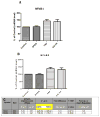
TNFα receptors are constitutively overexpressed in tumor cells, correlating to sustain elevated NFκB and monocyte chemotactic protein-1 (MCP-1/CCL2) expression. The elevation of CCL2 evokes aggressive forms of malignant tumors marked by tumor associated macrophage (TAM) recruitment, cell proliferation, invasion and angiogenesis. Previously, we have shown that the organo-sulfur compound diallyl disulfide (DADS) found in garlic (Allium sativum) attenuates TNFα induced CCL2 production in MDA-MB-231 cells. In the current study, we explored the signaling pathways responsible for DADS suppressive effect on TNFα mediated CCL2 release using PCR Arrays, RT-PCR and western blots. The data in this study show that TNFα initiates a rise in NFκB mRNA, which is not reversed by DADS. However, TNFα induced heightened expression of IKKε and phosphorylated ERK. The expression of these proteins corresponds to increased CCL2 release that can be attenuated by DADS. CCL2 induction by TNFα was also lessened by inhibitors of p38 (SB202190) and MEK (U0126) but not JNK (SP 600125), all of which were suppressed by DADS. In conclusion, the obtained results indicate that DADS down regulates TNFα invoked CCL2 production primarily through reduction of IKKε and phosphorylated-ERK, thereby impairing MAPK/ERK, and NFκB pathway signaling. Future research will be required to evaluate the effects of DADS on the function and expression of TNFα surface receptors.
Keywords: Diallyl disulfide; Map kinase b; Monocyte chemoattractant protein 1; Nuclear factor kappa b; Tumor necrosis factor alpha.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Zlotnik A. Chemokines in neoplastic progression. Seminars in cancer biology. 2004;14:181–5. - PubMed
-
- Rossi D, Zlotnik A. The biology of chemokines and their receptors. Annual review of immunology. 2000;18:217–42. - PubMed
-
- Jaattela M. Biologic activities and mechanisms of action of tumor necrosis factor-alpha/cachectin. Laboratory investigation; a journal of technical methods and pathology. 1991;64:724–42. - PubMed
-
- Balkwill F. TNF-alpha in promotion and progression of cancer. Cancer metastasis reviews. 2006;25:409–16. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

