Endocardial Brg1 disruption illustrates the developmental origins of semilunar valve disease
- PMID: 26100917
- PMCID: PMC4694578
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2015.06.015
Endocardial Brg1 disruption illustrates the developmental origins of semilunar valve disease
Abstract
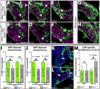
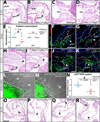
The formation of intricately organized aortic and pulmonic valves from primitive endocardial cushions of the outflow tract is a remarkable accomplishment of embryonic development. While not always initially pathologic, developmental semilunar valve (SLV) defects, including bicuspid aortic valve, frequently progress to a disease state in adults requiring valve replacement surgery. Disrupted embryonic growth, differentiation, and patterning events that "trigger" SLV disease are coordinated by gene expression changes in endocardial, myocardial, and cushion mesenchymal cells. We explored roles of chromatin regulation in valve gene regulatory networks by conditional inactivation of the Brg1-associated factor (BAF) chromatin remodeling complex in the endocardial lineage. Endocardial Brg1-deficient mouse embryos develop thickened and disorganized SLV cusps that frequently become bicuspid and myxomatous, including in surviving adults. These SLV disease-like phenotypes originate from deficient endocardial-to-mesenchymal transformation (EMT) in the proximal outflow tract (pOFT) cushions. The missing cells are replaced by compensating neural crest or other non-EMT-derived mesenchyme. However, these cells are incompetent to fully pattern the valve interstitium into distinct regions with specialized extracellular matrices. Transcriptomics reveal genes that may promote growth and patterning of SLVs and/or serve as disease-state biomarkers. Mechanistic studies of SLV disease genes should distinguish between disease origins and progression; the latter may reflect secondary responses to a disrupted developmental system.
Keywords: BAF complex; Bicuspid aortic valve; Brg1; Chromatin remodeling; Endocardial cushions; Endocardial-to-mesenchymal transformation; Outflow tract; Semilunar valves; Valve disease.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures





References
-
- Angelini A, Ho SY, Anderson RH, Devine WA, Zuberbuhler JR, Becker AE, Davies MJ. The morphology of the normal aortic valve as compared with the aortic valve having two leaflets. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1989;98:362–367. - PubMed
-
- Boles NC, Hirsch SE, Le S, Corneo B, Najm F, Minotti AP, Wang Q, Lotz S, Tesar PJ, Fasano CA. NPTX1 Regulates Neural Lineage Specification from Human Pluripotent Stem Cells. Cell Reports. 2014;6:724–736. - PubMed
-
- Broom ND. The observation of collagen and elastin structures in wet whole mounts of pulmonary and aortic leaflets. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1978;75:121–130. - PubMed
-
- Bultman S, Gebuhr T, Yee D, La Mantia C, Nicholson J, Gilliam A, Randazzo F, Metzger D, Chambon P, Crabtree G, et al. A Brg1 null mutation in the mouse reveals functional differences among mammalian SWI/SNF complexes. Molecular Cell. 2000;6:1287–1295. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

