Mucoepidermoid carcinoma in a thyroglossal duct remnant
- PMID: 26101054
- PMCID: PMC4529606
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2015.04.028
Mucoepidermoid carcinoma in a thyroglossal duct remnant
Abstract
Introduction: Thyroglossal duct cysts (TDC) are common midline neck swellings resulting from embryological remnants of the thyroglossal duct. They often contain ectopic thyroid tissue and malignant transformation has been reported, most commonly to papillary thyroid carcinoma. Mucoepidermoid carcinoma (MEC) usually occurs in the salivary glands and only rarely in the thyroid. This is the first case of a MEC occurring within a thyroglossal duct remnant.
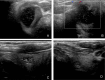
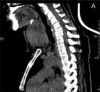
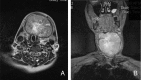
Presentation of a case: A 73 year old lady presented with a thyroglossal duct cyst. She declined surgical excision, as she was adamant she wanted to avoid surgery. The neck mass rapidly enlarged at two years following initial diagnosis. Fine needle aspiration cytology was suspicious for carcinoma. She underwent total thyroidectomy and selective central compartment neck dissection with adjuvant radiotherapy. She remains alive and well two years post treatment.
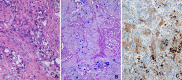
Discussion: Mucoepidermoid carcinoma is the most common malignant neoplasm of salivary glands, although it has rarely been reported in diverse locations including the thyroid, lung and pancreas. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first reported case of mucoepidermoid carcinoma arising from a thyroglossal duct remnant.
Conclusion: This case adds weight to the literature favouring surgical excision of thyroglossal duct remnants due to the risk of malignant transformation.
Keywords: Head and neck neoplasm; Mucoepidermoid carcinoma; Salivary gland; Thyroglossal duct.
Copyright © 2015 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Robot-assisted Sistrunk's operation, total thyroidectomy, and neck dissection via a transaxillary and retroauricular (TARA) approach in papillary carcinoma arising in thyroglossal duct cyst and thyroid gland.Ann Surg Oncol. 2012 Dec;19(13):4259-61. doi: 10.1245/s10434-012-2674-y. Epub 2012 Oct 16. Ann Surg Oncol. 2012. PMID: 23070784
-
Invasive Thyroglossal Duct Cyst Papillary Carcinoma: A Case Report and Review of the Literature.Am J Case Rep. 2018 Jun 28;19:757-762. doi: 10.12659/AJCR.907313. Am J Case Rep. 2018. PMID: 29950556 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Arising From a Thyroglossal Duct Cyst: A Case Report.Cureus. 2025 May 12;17(5):e83982. doi: 10.7759/cureus.83982. eCollection 2025 May. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40519419 Free PMC article.
-
[Thyroglossal duct cyst carcinoma: The rational behind performing a total thyroidectomy].Rev Med Brux. 2016;37(6):495-497. Rev Med Brux. 2016. PMID: 28525179 French.
-
Thyroglossal Duct Cyst Carcinomas in Pediatric Patients: Report of Two Cases with a Comprehensive Literature Review.Head Neck Pathol. 2017 Dec;11(4):442-449. doi: 10.1007/s12105-017-0807-0. Epub 2017 Mar 14. Head Neck Pathol. 2017. PMID: 28293858 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Malignant Cystic Midline Neck Mass.OTO Open. 2019 May 13;3(2):2473974X19849046. doi: 10.1177/2473974X19849046. eCollection 2019 Apr-Jun. OTO Open. 2019. PMID: 31535072 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Thyroglossal Duct Cyst Carcinoma: Lessons from a 20-Case Series.Indian J Surg Oncol. 2023 Sep;14(3):609-618. doi: 10.1007/s13193-023-01720-0. Epub 2023 Feb 28. Indian J Surg Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37900628 Free PMC article.
-
Salivary-Like Tumors of the Thyroid: A Comprehensive Review of Three Rare Carcinomas.Head Neck Pathol. 2021 Mar;15(1):212-224. doi: 10.1007/s12105-020-01193-5. Epub 2020 Jun 19. Head Neck Pathol. 2021. PMID: 32562215 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Squamous Differentiation in the Thyroid: Metaplasia, Neoplasia, or Bystander?Int J Surg Pathol. 2022 Jun;30(4):385-392. doi: 10.1177/10668969211065126. Epub 2021 Dec 13. Int J Surg Pathol. 2022. PMID: 34894811 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Al-Khateeb T.H., Al Zoubi F. Congenital neck masses: a descriptive retrospective study of 252 cases. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2007;65(November (11)):2242–2247. - PubMed
-
- Mondin V., Ferlito A., Muzzi E., Silver C.E., Fagan J.J., Devaney K.O., Rinaldo A. Thyroglossal duct cyst: personal experience and literature review. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2008;35:11–25. - PubMed
-
- Barnes L. 1st ed. IARC Pr.; Lyon: 2005. Pathology and Genetics of Head and Neck Tumours.
-
- Rossi E.D., Martini M., Straccia P., Cocomazzi A., Pennacchia I. Thyroglossal duct cyst cancer most likely arises from a thyroid gland remnant. Virchows Arch. 2014;465(July (1)):67–72. - PubMed
-
- Kay S. Mucoepidermoid carcinoma of the esophagus: report of two cases. Cancer. 1968;22(5):1053–1059. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

