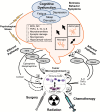
Neurocognitive Impairment as One Facet of Cancer-Related Sickness Behavior Symptoms
- PMID: 26101332
- PMCID: PMC4609561
- DOI: 10.1093/jnci/djv176
Neurocognitive Impairment as One Facet of Cancer-Related Sickness Behavior Symptoms
Comment on
-
Inflammatory Biomarkers, Comorbidity, and Neurocognition in Women With Newly Diagnosed Breast Cancer.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2015 Jun 22;107(8):djv131. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djv131. Print 2015 Aug. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2015. PMID: 26101331 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical