Depression in Rheumatoid Arthritis and its relation to disease activity
- PMID: 26101498
- PMCID: PMC4476349
- DOI: 10.12669/pjms.312.6589
Depression in Rheumatoid Arthritis and its relation to disease activity
Abstract
Objectives: To determine the level of depression in Rheumatoid Arthritis and its relationship with severity of Rheumatoid Arthritis.
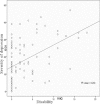
Methods: This cross sectional analytical study was conducted from March 2014 to May 2014. Total 102 cases of Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) diagnosed as per ACR (American College of Rheumatology) 1987 criteria were enrolled from Rheumatology Department, Fatima Memorial Hospital. Severity of Rheumatoid Arthritis was assessed by Health Assessment Questionnaire (HAQ) and disease activity score (DAS - 28) while severity of depression was measured by Beck Depression Inventory (BDI) scale II questionnaire. The relationship between depression and disease activity (severity) of Rheumatoid Arthritis was assessed by calculating correlation coefficient between depression, disease activity score (DAS 28) of Rheumatoid Arthritis and health assessment questionnaire (HAQ).
Results: Out of 102 patients, 77(75.5%) were females and 25(24.5%) males. The mean age of patients was 43.5± 11.9 years and the mean duration of disease was 7.8 ± 5.5 years.71.5% of Rheumatoid Arthritis patients were found to have some degree of depression and this was directly related to the severity of disease. Moderate and severe depression were present in 23 (22.5%) and 19(18.6%) patients respectively.
Conclusion: In this study, almost three-fourths of Rheumatoid Arthritis patients were found to have depression. There was a strong association between Rheumatoid Arthritis disease activity and the level of depression. So it is imperative for clinicians treating Rheumatoid Arthritis patients to screen them for co morbid depression and manage it accordingly.
Keywords: BDI scale; DAS - 28; Depression; Rheumatoid Arthritis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The association of disease activity with depression and sleep quality in patients with rheumatoid arthritis in Hong Kong.Int J Rheum Dis. 2023 Dec;26(12):2543-2550. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.14957. Epub 2023 Nov 3. Int J Rheum Dis. 2023. PMID: 37923558
-
Evaluation of sexual dysfunction in women with rheumatoid arthritis: a controlled study.J Sex Med. 2012 Oct;9(10):2664-70. doi: 10.1111/j.1743-6109.2012.02882.x. Epub 2012 Aug 20. J Sex Med. 2012. PMID: 22906191
-
Are we missing the diagnosis of depression in patients with rheumatoid arthritis at a tertiary care facility?Pak J Med Sci. 2017 Mar-Apr;33(2):300-305. doi: 10.12669/pjms.332.11856. Pak J Med Sci. 2017. PMID: 28523026 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence and Correlation of Depressive Symptoms with Functional Scores, Therapy and Disease Activity among Croatian Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Preliminary Study.Psychiatr Danub. 2018 Dec;30(4):452-458. doi: 10.24869/psyd.2018.452. Psychiatr Danub. 2018. PMID: 30439805
-
The American College of Rheumatology (ACR) Core Data Set and derivative "patient only" indices to assess rheumatoid arthritis.Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2005 Sep-Oct;23(5 Suppl 39):S109-13. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2005. PMID: 16273794 Review.
Cited by
-
Association analysis of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor-A (VEGF-A) polymorphism in rheumatoid arthritis using computational approaches.Sci Rep. 2023 Dec 11;13(1):21957. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-47780-8. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 38081836 Free PMC article.
-
Trends in Opioid Use in a Cohort of Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis.Pain Res Manag. 2020 Jul 16;2020:3891436. doi: 10.1155/2020/3891436. eCollection 2020. Pain Res Manag. 2020. PMID: 32724487 Free PMC article.
-
Sexual Health and Dysfunction in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Cross-sectional Single-Center Study.Sex Med. 2020 Dec;8(4):615-630. doi: 10.1016/j.esxm.2020.07.004. Epub 2020 Sep 8. Sex Med. 2020. PMID: 32912833 Free PMC article.
-
Silymarin Supplementation in Active Rheumatoid Arthritis: Outcomes of a Pilot Randomized Controlled Clinical Study.Medicina (Kaunas). 2024 Jun 18;60(6):999. doi: 10.3390/medicina60060999. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024. PMID: 38929616 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Prevalence of depression among Iranian patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Open Access Rheumatol. 2019 Feb 13;11:53-59. doi: 10.2147/OARRR.S191459. eCollection 2019. Open Access Rheumatol. 2019. PMID: 30863193 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Saleem B, Brown AK, Quinn M, Karim Z, Hensor EM, Conaghan P, et al. Can flare be predicted in DMARD treated RA patients in remission, and is it important? A cohort study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2012;71:1316–1321. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2011-200548. - PubMed
-
- Alam SM, Kidwai AA, Jafri SR. Jour Pak med assoc. Epidemiology of rheumatoid arthritis in a tertiary care unit. Karachi, Pak. J Pak Med Assoc. 2011;61(2):123–126. - PubMed
-
- Theofilou P. Psychological Impact of Rheumatoid Arthritis on Patient's Health. J Arthritis. 2012;1(1) doi:10.4172/2167-7921.1000e102.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources