Steroid-induced ischemic bone necrosis of femoral head: Treatment strategies
- PMID: 26101514
- PMCID: PMC4476365
- DOI: 10.12669/pjms.312.6592
Steroid-induced ischemic bone necrosis of femoral head: Treatment strategies
Abstract
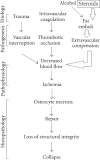
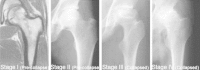
Fat hypertrophy, intravascular coagulation, and fat emboli are important risk factors of steroid-induced ischemic bone necrosis (SI-IBN) which may develop during the initial one year after commencing the use of steroids. This pathology is best studied by MRI, particularly for its staging. The cautious strategies such as low dose, oral route, short duration of steroid usage, use of steroid sparing agent, and alcohol avoidance should be followed as a traditional therapy. The objective of this review article was to recognize and evaluate various Treatment strategies for steroid-induced ischemic bone necrosis of femoral head.
Literature search: Various electronic databases including PubMed, Google and Cochrane library were comprehensively searched for articles on steroid-induced ischemic bone necrosis of femoral head and its treatment strategies. Ninety four articles were reviewed, examined and importantly appraised and the most appropriate 32 papers were used to write this review article.
Conclusion: Bisphosphonates, alendronate, and hyperbaric oxygen (HBO) treatments have been reported to be effective against IBN. To recommend the regular use of bisphosphonate in IBN patients, more evidences with a larger number of patients are required to verify its therapeutic effectiveness. Core decompression, osteotomy, bone graft and tantalum rod are the surgical approaches for the management of IBN. Advance form of IBN (bone tissue collapse) is advised to be treated with arthroplasty which should be durable, particularly in young patients.
Keywords: Arthoplasty; Bone collapse; Ischemic bone necrosis; Steroid; Vasculature.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[STEROID-INDUCED OSTEONECROSES OF FEMORAL HEAD].Georgian Med News. 2020 Jan;(298):21-27. Georgian Med News. 2020. PMID: 32141842 Russian.
-
[Treatment of avascular necrosis of the femoral head by lesions clearance, compact bone grafting, and porous tantalum rod implantation].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2011 Nov;25(11):1335-8. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2011. PMID: 22229188 Chinese.
-
Key pathway to prevent the collapse of femoral head in osteonecrosis.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2015 Aug;19(15):2766-74. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26241528
-
What is the rate of patients undergoing a total hip arthroplasty after core decompression and insertion of a tantalum rod in osteonecrosis of the femoral head: a systematic review.Int Orthop. 2018 Jul;42(7):1631-1638. doi: 10.1007/s00264-018-3961-4. Epub 2018 May 4. Int Orthop. 2018. PMID: 29728733
-
RISK-FACTORS, PATHOGENESIS, AND PHARMACEUTICAL APPROACHES FOR TREATMENT OF STEROID-INDUCED BONE INFARCTION OF FEMORAL HEAD.Acta Pol Pharm. 2016 May-Jun;73(3):557-63. Acta Pol Pharm. 2016. PMID: 27476272 Review.
Cited by
-
A 12-year follow-up study of combined treatment of post-severe acute respiratory syndrome patients with femoral head necrosis.Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2017 Oct 19;13:1449-1454. doi: 10.2147/TCRM.S140694. eCollection 2017. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2017. PMID: 29089773 Free PMC article.
-
Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1 4G/5G Polymorphism Contributes to Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head Susceptibility: Evidence from a Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Arch Bone Jt Surg. 2018 Nov;6(6):468-477. Arch Bone Jt Surg. 2018. PMID: 30637301 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Early detection of steroid-induced femoral head necrosis using 99mTc-Cys-Annexin V-based apoptosis imaging in a rabbit model.Mol Med. 2020 Dec 3;26(1):120. doi: 10.1186/s10020-020-00248-1. Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 33272196 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of hub genes and therapeutic drugs in osteonecrosis of the femoral head through integrated bioinformatics analysis and literature mining.Sci Rep. 2023 Jul 24;13(1):11972. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-39258-4. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37488209 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical reports of surgical dislocation of the hip with sequestrum clearance and impacting bone graft for grade IIIA-IIIB aseptic necrosis of femoral head (ANFH) patients.Oncotarget. 2017 Jul 25;8(30):50084-50090. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.15095. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28177916 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Assouline-Dayan Y, Chang C, Greenspan A, Shoenfeld Y, Gershwin ME. Pathogenesis and natural history of osteonecrosis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2002;32(2):94–124. - PubMed
-
- Wang Y, Li Y, Mao K, Li J, Cui Q, Wang GY. Alcohol-induced adipogenesis in bone and marrow: a possible mechanism for osteonecrosis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003;410:213–224. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources