Herbal SGR Formula Prevents Acute Ethanol-Induced Liver Steatosis via Inhibition of Lipogenesis and Enhancement Fatty Acid Oxidation in Mice
- PMID: 26101535
- PMCID: PMC4458561
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/613584
Herbal SGR Formula Prevents Acute Ethanol-Induced Liver Steatosis via Inhibition of Lipogenesis and Enhancement Fatty Acid Oxidation in Mice
Abstract
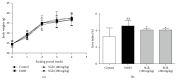
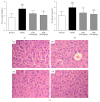
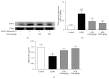
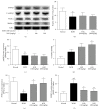
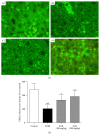
Our previous study indicated that herbal SGR formula partially attenuates ethanol-induced fatty liver, but the underlying mechanisms remain unclear. In the present study, mice were pretreated with SGR (100 and 200 mg/kg/d bw) for 30 d before being exposed to ethanol (4.8 g/kg bw). The biochemical indices and histopathological changes were examined to evaluate the protective effects and to explore potential mechanisms by investigating the adiponectin, tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), peroxisome proliferators-activated receptor-α (PPAR-α), sterol regulatory element binding protein-1c (SREBP-1c), adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK), and so forth. Results showed that SGR pretreatment markedly inhibited acute ethanol-induced liver steatosis, significantly reduced serum and hepatic triglyceride (TG) level, and improved classic histopathological changes. SGR suppressed the protein expression of hepatic SREBP-1c and TNF-α and increased adiponectin, PPAR-α, and AMPK phosphorylation in the liver. Meanwhile, acute toxicity tests showed that no death or toxic side effects within 14 days were observed upon oral administration of the extracts at a dose of 16 g/kg body wt. These results demonstrate that SGR could protect against acute alcohol-induced liver steatosis without any toxic side effects. Therefore, our studies provide novel molecular insights into the hepatoprotective effect of SGR formula, which may be exploited as a therapeutic agent for ethanol-induced hepatosteatosis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Chronic treatment with the modified Longdan Xiegan Tang attenuates olanzapine-induced fatty liver in rats by regulating hepatic de novo lipogenesis and fatty acid beta-oxidation-associated gene expression mediated by SREBP-1c, PPAR-alpha and AMPK-alpha.J Ethnopharmacol. 2019 Mar 25;232:176-187. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2018.12.034. Epub 2018 Dec 24. J Ethnopharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30590197
-
Honokiol reverses alcoholic fatty liver by inhibiting the maturation of sterol regulatory element binding protein-1c and the expression of its downstream lipogenesis genes.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2009 Apr 1;236(1):124-30. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2008.12.030. Epub 2009 Jan 24. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19371623
-
Garlic oil alleviated ethanol-induced fat accumulation via modulation of SREBP-1, PPAR-α, and CYP2E1.Food Chem Toxicol. 2012 Mar;50(3-4):485-91. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2011.11.030. Epub 2011 Nov 26. Food Chem Toxicol. 2012. PMID: 22138249
-
n-3 Polyunsaturated fatty acids for the management of alcoholic liver disease: A critical review.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2019;59(sup1):S116-S129. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2018.1544542. Epub 2018 Dec 22. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2019. PMID: 30580553 Review.
-
Adiponectin and alcoholic fatty liver disease.IUBMB Life. 2008 Dec;60(12):790-7. doi: 10.1002/iub.124. IUBMB Life. 2008. PMID: 18709650 Review.
Cited by
-
Small heterodimer partner deficiency exacerbates binge drinking‑induced liver injury via modulation of natural killer T cell and neutrophil infiltration.Mol Med Rep. 2018 Apr;17(4):4989-4998. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2018.8505. Epub 2018 Jan 26. Mol Med Rep. 2018. PMID: 29393499 Free PMC article.
-
The Impacts of Herbal Medicines and Natural Products on Regulating the Hepatic Lipid Metabolism.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Mar 24;11:351. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00351. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32265720 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

