Sevoflurane Induces DNA Damage Whereas Isoflurane Leads to Higher Antioxidative Status in Anesthetized Rats
- PMID: 26101770
- PMCID: PMC4458518
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/264971
Sevoflurane Induces DNA Damage Whereas Isoflurane Leads to Higher Antioxidative Status in Anesthetized Rats
Abstract
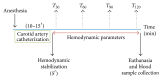
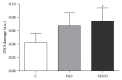
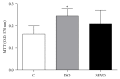
Taking into account that there are controversial antioxidative effects of inhalational anesthetics isoflurane and sevoflurane and absence of comparison of genotoxicity of both anesthetics in animal model, the aim of this study was to compare DNA damage and antioxidant status in Wistar rats exposed to a single time to isoflurane or sevoflurane. The alkaline single-cell gel electrophoresis assay (comet assay) was performed in order to evaluate DNA damage in whole blood cells of control animals (unexposed; n = 6) and those exposed to 2% isoflurane (n = 6) or 4% sevoflurane (n = 6) for 120 min. Plasma antioxidant status was determined by 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay. There was no statistically significant difference between isoflurane and sevoflurane groups regarding hemodynamic and temperature variables (P > 0.05). Sevoflurane significantly increased DNA damage compared to unexposed animals (P = 0.02). In addition, Wistar rats anesthetized with isoflurane showed higher antioxidative status (MTT) than control group (P = 0.019). There were no significant differences in DNA damage or antioxidant status between isoflurane and sevoflurane groups (P > 0.05). In conclusion, our findings suggest that, in contrast to sevoflurane exposure, isoflurane increases systemic antioxidative status, protecting cells from DNA damage in rats.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Differential protective effects of anaesthesia with sevoflurane or isoflurane: an animal experimental model simulating liver transplantation.Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2014 Dec;31(12):695-700. doi: 10.1097/EJA.0000000000000127. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2014. PMID: 25105848
-
Comparison of genotoxicity of sevoflurane and isoflurane in human lymphocytes studied in vivo using the comet assay.Mutat Res. 2001 May 31;492(1-2):99-107. doi: 10.1016/s1383-5718(01)00159-0. Mutat Res. 2001. PMID: 11377249
-
Impact of Volatile Anesthetics on Oxidative Stress and Inflammation.Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:242709. doi: 10.1155/2015/242709. Epub 2015 May 25. Biomed Res Int. 2015. PMID: 26101769 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Single vital capacity inhalational anaesthetic induction in adults--isoflurane vs sevoflurane.Can J Anaesth. 1998 Oct;45(10):949-53. doi: 10.1007/BF03012302. Can J Anaesth. 1998. PMID: 9836031 Clinical Trial.
-
[Use of sevoflurane in neuroanesthesiology].Anesteziol Reanimatol. 2006 Mar-Apr;(2):25-32. Anesteziol Reanimatol. 2006. PMID: 16758940 Review. Russian.
Cited by
-
Effects of sevoflurane and isoflurane on acute myocardial infarction model establishment in mice.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2025 Apr 3;42:102000. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2025.102000. eCollection 2025 Jun. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2025. PMID: 40236295 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of repeated doses of xylazine-ketamine and medetomidineketamine anesthesia on DNA damage in the liver and kidney.Acta Cir Bras. 2023 Oct 30;38:e385723. doi: 10.1590/acb385723. eCollection 2023. Acta Cir Bras. 2023. PMID: 37909595 Free PMC article.
-
Safety of general anaesthetics on the developing brain: are we there yet?BJA Open. 2022 May 17;2:100012. doi: 10.1016/j.bjao.2022.100012. eCollection 2022 Jun. BJA Open. 2022. PMID: 37588272 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Sevoflurane on Natural Killer Group 2, Member D-Mediated Immune Response in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: An In Vitro Study.Med Sci Monit. 2020 Nov 3;26:e926395. doi: 10.12659/MSM.926395. Med Sci Monit. 2020. PMID: 33139690 Free PMC article.
-
Sevoflurane Exacerbates Cognitive Impairment Induced by Aβ 1-40 in Rats through Initiating Neurotoxicity, Neuroinflammation, and Neuronal Apoptosis in Rat Hippocampus.Mediators Inflamm. 2018 Oct 9;2018:3802324. doi: 10.1155/2018/3802324. eCollection 2018. Mediators Inflamm. 2018. PMID: 30402039 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Green C. J. Anaesthetic gases and health risks to laboratory personnel: a review. Laboratory Animals. 1981;15(4):397–403. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

