An integrated view of cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity
- PMID: 26101797
- PMCID: PMC4516600
- DOI: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2015.06.012
An integrated view of cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity
Abstract
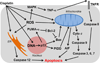
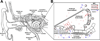
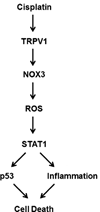
Cisplatin is one of the most widely-used drugs to treat cancers. However, its nephrotoxic and ototoxic side-effects remain major clinical limitations. Recent studies have improved our understanding of the molecular mechanisms of cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity. While cisplatin binding to DNA is the major cytotoxic mechanism in proliferating (cancer) cells, nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity appear to result from toxic levels of reactive oxygen species and protein dysregulation within various cellular compartments. In this review, we discuss molecular mechanisms of cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity. We also discuss potential clinical strategies to prevent nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity and their current limitations.
Keywords: Cisplatin; Intracellular mechanisms; Nephrotoxicity; Ototoxicity.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Aabo K, Adams M, Adnitt P, Alberts DS, Athanazziou A, Barley V, Bell DR, Bianchi U, Bolis G, Brady MF, Brodovsky HS, Bruckner H, Buyse M, Canetta R, Chylak V, Cohen CJ, Colombo N, Conte PF, Crowther D, Edmonson JH, Gennatas C, Gilbey E, Gore M, Guthrie D, Yeap BY, et al. Chemotherapy in advanced ovarian cancer: four systematic meta-analyses of individual patient data from 37 randomized trials. Advanced Ovarian Cancer Trialists’ Group. Br. J. Cancer. 1998;78:1479–1487. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arany I, Megyesi JK, Kaneto H, Price PM, Safirstein RL. Cisplatin-induced cell death is EGFR/src/ERK signaling dependent in mouse proximal tubule cells. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2004;287:F543–F549. - PubMed
-
- Assad JA, Shepherd GM, Corey DP. Tip-link integrity and mechanical transduction in vertebrate hair cells. Neuron. 1991;7:985–994. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

