Rare coding mutations identified by sequencing of Alzheimer disease genome-wide association studies loci
- PMID: 26101835
- PMCID: PMC4546546
- DOI: 10.1002/ana.24466
Rare coding mutations identified by sequencing of Alzheimer disease genome-wide association studies loci
Abstract
Objective: To detect rare coding variants underlying loci detected by genome-wide association studies (GWAS) of late onset Alzheimer disease (LOAD).
Methods: We conducted targeted sequencing of ABCA7, BIN1, CD2AP, CLU, CR1, EPHA1, MS4A4A/MS4A6A, and PICALM in 3 independent LOAD cohorts: 176 patients from 124 Caribbean Hispanics families, 120 patients and 33 unaffected individuals from the 129 National Institute on Aging LOAD Family Study; and 263 unrelated Canadian individuals of European ancestry (210 sporadic patients and 53 controls). Rare coding variants found in at least 2 data sets were genotyped in independent groups of ancestry-matched controls. Additionally, the Exome Aggregation Consortium was used as a reference data set for population-based allele frequencies.
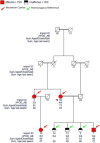
Results: Overall we detected a statistically significant 3.1-fold enrichment of the nonsynonymous mutations in the Caucasian LOAD cases compared with controls (p = 0.002) and no difference in synonymous variants. A stop-gain mutation in ABCA7 (E1679X) and missense mutation in CD2AP (K633R) were highly significant in Caucasian LOAD cases, and mutations in EPHA1 (P460L) and BIN1 (K358R) were significant in Caribbean Hispanic families with LOAD. The EPHA1 variant segregated completely in an extended Caribbean Hispanic family and was also nominally significant in the Caucasians. Additionally, BIN1 (K358R) segregated in 2 of the 6 Caribbean Hispanic families where the mutations were discovered.
Interpretation: Targeted sequencing of confirmed GWAS loci revealed an excess burden of deleterious coding mutations in LOAD, with the greatest burden observed in ABCA7 and BIN1. Identifying coding variants in LOAD will facilitate the creation of tractable models for investigation of disease-related mechanisms and potential therapies.
© 2015 The Authors Annals of Neurology published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of American Neurological Association.
Figures

References
-
- Lambert JC, Heath S, Even G, et al. Genome‐wide association study identifies variants at CLU and CR1 associated with Alzheimer's disease. Nat Genet 2009;41:1094–1099. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- U24 AG021886/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG008702/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01AG07232/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AG056270/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 089703/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 AG015473/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG041797/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG037212/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG015473/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U24AG026395/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG041797/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- MC_G1000734/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- P01 AG007232/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U24AG21886/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AG015473/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AG026395/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 081864/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R37AG15473/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

