Immunization with Heat Shock Protein A and γ-Glutamyl Transpeptidase Induces Reduction on the Helicobacter pylori Colonization in Mice
- PMID: 26102080
- PMCID: PMC4478016
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0130391
Immunization with Heat Shock Protein A and γ-Glutamyl Transpeptidase Induces Reduction on the Helicobacter pylori Colonization in Mice
Abstract
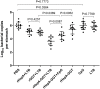
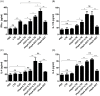
The human gastric pathogen Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) is a successful colonizer of the stomach. H. pylori infection strongly correlates with the development and progression of chronic gastritis, peptic ulcer disease, and gastric malignances. Vaccination is a promising strategy for preventing H. pylori infection. In this study, we evaluated the candidate antigens heat shock protein A (HspA) and H. pylori γ-glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT) for their effectiveness in development of subunit vaccines against H. pylori infection. rHspA, rGGT, and rHspA-GGT, a fusion protein based on HspA and GGT, were constructed and separately expressed in Escherichia coli and purified. Mice were then immunized intranasally with these proteins, with or without adjuvant. Immunized mice exhibited reduced bacterial colonization in stomach. The highest reduction in bacterial colonization was seen in mice immunized with the fusion protein rHspA-GGT when paired with the mucosal adjuvant LTB. Protection against H. pylori colonization was mediated by a strong systemic and localized humoral immune response, as well as a balanced Th1/Th2 cytokine response. In addition, immunofluorescence microscopy confirmed that rHspA-GGT specific rabbit antibodies were able to directly bind H. pylori in vitro. These results suggest antibodies are essential to the protective immunity associated with rHspA-GGT immunization. In summary, our results suggest HspA and GGT are promising vaccine candidates for protection against H. pylori infection.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Protective efficacy of vaccines based on the Helicobacter suis urease subunit B and γ-glutamyl transpeptidase.Vaccine. 2013 Jul 11;31(32):3250-6. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2013.05.047. Epub 2013 May 23. Vaccine. 2013. PMID: 23707444
-
Heat shock protein complex vaccination induces protection against Helicobacter pylori without exogenous adjuvant.Vaccine. 2014 Apr 25;32(20):2350-8. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2014.02.051. Epub 2014 Mar 10. Vaccine. 2014. PMID: 24625340
-
Mucosal immunization with a urease B DNA vaccine induces innate and cellular immune responses against Helicobacter pylori.Helicobacter. 2006 Apr;11(2):113-22. doi: 10.1111/j.1523-5378.2006.00385.x. Helicobacter. 2006. PMID: 16579841
-
The design of vaccines against Helicobacter pylori and their development.Annu Rev Immunol. 2001;19:523-63. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.19.1.523. Annu Rev Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11244046 Review.
-
Bacterial Gamma-Glutamyl Transpeptidase, an Emerging Biocatalyst: Insights Into Structure-Function Relationship and Its Biotechnological Applications.Front Microbiol. 2021 Apr 9;12:641251. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.641251. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33897647 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The chimeric UreB, FliD and Omp18 proteins for a sensitive and specific diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori infections.Iran J Microbiol. 2024 Jun;16(3):357-365. doi: 10.18502/ijm.v16i3.15768. Iran J Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39005599 Free PMC article.
-
Developing a potent vaccine against Helicobacter pylori: critical considerations and challenges.Expert Rev Mol Med. 2024 Nov 25;27:e12. doi: 10.1017/erm.2024.19. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 39584502 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of B-Cell Epitopes of HspA from Helicobacter pylori and Detection of Epitope Antibody Profiles in Naturally Infected Persons.Vaccines (Basel). 2021 Dec 31;10(1):65. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10010065. Vaccines (Basel). 2021. PMID: 35062726 Free PMC article.
-
E. coli Enterotoxin LtB Enhances Vaccine-Induced Anti-H. pylori Protection by Promoting Leukocyte Migration into Gastric Mucus via Inflammatory Lesions.Cells. 2019 Aug 27;8(9):982. doi: 10.3390/cells8090982. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31461854 Free PMC article.
-
Live Attenuated Measles Virus Vaccine Expressing Helicobacter pylori Heat Shock Protein A.Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2020 Sep 23;19:136-148. doi: 10.1016/j.omto.2020.09.006. eCollection 2020 Dec 16. Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2020. PMID: 33145397 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ramirez-Ramos A, Gilman RH, Leon-Barua R, Recavarren-Arce S, Watanabe J, Salazar G, et al. (1997) Rapid recurrence of Helicobacter pylori infection in Peruvian patients after successful eradication. Gastrointestinal Physiology Working Group of the Universidad Peruana Cayetano Heredia and The Johns Hopkins University. Clin Infect Dis 25: 1027–1031. - PubMed
-
- Cameron EA, Bell GD (2005) Long-term follow-up of Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy in Vietnam: reinfection and clinical outcome. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 22: 76–77. - PubMed
-
- (1983) Unidentified curved bacilli on gastric epithelium in active chronic gastritis. Lancet 1: 1273–1275. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

