Citizen Sensors for SHM: Towards a Crowdsourcing Platform
- PMID: 26102490
- PMCID: PMC4507648
- DOI: 10.3390/s150614591
Citizen Sensors for SHM: Towards a Crowdsourcing Platform
Abstract
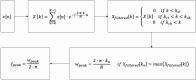
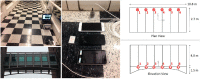
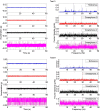
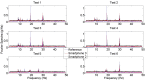
This paper presents an innovative structural health monitoring (SHM) platform in terms of how it integrates smartphone sensors, the web, and crowdsourcing. The ubiquity of smartphones has provided an opportunity to create low-cost sensor networks for SHM. Crowdsourcing has given rise to citizen initiatives becoming a vast source of inexpensive, valuable but heterogeneous data. Previously, the authors have investigated the reliability of smartphone accelerometers for vibration-based SHM. This paper takes a step further to integrate mobile sensing and web-based computing for a prospective crowdsourcing-based SHM platform. An iOS application was developed to enable citizens to measure structural vibration and upload the data to a server with smartphones. A web-based platform was developed to collect and process the data automatically and store the processed data, such as modal properties of the structure, for long-term SHM purposes. Finally, the integrated mobile and web-based platforms were tested to collect the low-amplitude ambient vibration data of a bridge structure. Possible sources of uncertainties related to citizens were investigated, including the phone location, coupling conditions, and sampling duration. The field test results showed that the vibration data acquired by smartphones operated by citizens without expertise are useful for identifying structural modal properties with high accuracy. This platform can be further developed into an automated, smart, sustainable, cost-free system for long-term monitoring of structural integrity of spatially distributed urban infrastructure. Citizen Sensors for SHM will be a novel participatory sensing platform in the way that it offers hybrid solutions to transitional crowdsourcing parameters.
Keywords: Citizen Sensors; ambient vibration; crowdsourcing; mobile networks; modal identification; smartphone sensors; structural health monitoring.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Smartphone Prospects in Bridge Structural Health Monitoring, a Literature Review.Sensors (Basel). 2024 May 21;24(11):3287. doi: 10.3390/s24113287. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38894080 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Citizen sensors for SHM: use of accelerometer data from smartphones.Sensors (Basel). 2015 Jan 29;15(2):2980-98. doi: 10.3390/s150202980. Sensors (Basel). 2015. PMID: 25643056 Free PMC article.
-
Design and Validation of Android Smartphone Based Wireless Structural Vibration Monitoring System.Sensors (Basel). 2020 Aug 25;20(17):4799. doi: 10.3390/s20174799. Sensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32854409 Free PMC article.
-
Wireless Sensor Networks Composed of Standard Microcomputers and Smartphones for Applications in Structural Health Monitoring.Sensors (Basel). 2019 May 3;19(9):2070. doi: 10.3390/s19092070. Sensors (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31058871 Free PMC article.
-
A Review of Radio Frequency Identification Sensing Systems for Structural Health Monitoring.Materials (Basel). 2022 Nov 7;15(21):7851. doi: 10.3390/ma15217851. Materials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36363442 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Study of Building Safety Monitoring by Using Cost-Effective MEMS Accelerometers for Rapid After-Earthquake Assessment with Missing Data.Sensors (Basel). 2021 Nov 3;21(21):7327. doi: 10.3390/s21217327. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34770632 Free PMC article.
-
Smartphone Prospects in Bridge Structural Health Monitoring, a Literature Review.Sensors (Basel). 2024 May 21;24(11):3287. doi: 10.3390/s24113287. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38894080 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Design of a Mobile Low-Cost Sensor Network Using Urban Buses for Real-Time Ubiquitous Noise Monitoring.Sensors (Basel). 2016 Dec 29;17(1):57. doi: 10.3390/s17010057. Sensors (Basel). 2016. PMID: 28036065 Free PMC article.
-
Automated and Model-Free Bridge Damage Indicators with Simultaneous Multiparameter Modal Anomaly Detection.Sensors (Basel). 2020 Aug 22;20(17):4752. doi: 10.3390/s20174752. Sensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32842695 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Smartphone Inertial Sensor Performance for Cross-Platform Mobile Applications.Sensors (Basel). 2016 Apr 4;16(4):477. doi: 10.3390/s16040477. Sensors (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27049391 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Skolnik D., Lei Y., Yu E., Wallace J.W. Identification, model updating, and response prediction of an instrumented 15-story steel-frame building. Earthq. Spectra. 2006;22:781–802.
-
- Catbas F.N., Susoy M., Frangopol D.M. Structural health monitoring and reliability estimation: Long span truss bridge application with environmental monitoring data. Eng. Struct. 2008;30:2347–2359.
-
- Moaveni B., He X., Conte J.P., Restrepo J.I. Damage identification study of a seven-story full-scale building slice tested on the UCSD-NEES shake table. Struct. Saf. 2010;32:347–356.
-
- Gomez H.C., Fanning P.J., Feng M.Q., Lee S. Testing and long-term monitoring of a curved concrete box girder bridge. Eng. Struct. 2011;33:2861–2869.
-
- Ozer E., Soyoz S. Vibration-based damage detection and seismic performance assessment of bridges. Earthq. Spectra. 2015;31:137–157.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

