Effect of radiation dose reduction on image quality in adult head CT with noise-suppressing reconstruction system with a 256 slice MDCT
- PMID: 26103494
- PMCID: PMC5690139
- DOI: 10.1120/jacmp.v16i3.5360
Effect of radiation dose reduction on image quality in adult head CT with noise-suppressing reconstruction system with a 256 slice MDCT
Abstract
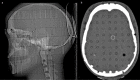
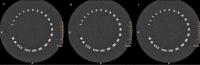
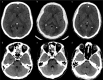
The purpose of our study was to investigate the effect of iterative reconstruction (IR) as a dose reduction system on the image quality (IQ) of the adult head computed tomography (CT) at various low-dose levels, and to identify ways of setting the amount of dose reduction. We performed two noncontrast low-dose (LD) adult head CT protocols modified by lowering the tube current with IR which were decided in the light of a group of phantom studies. Two groups of patients, each 100 underwent noncontrast head CT with LD-I and LD-II, respectively. These groups were compared with 100 consecutive standard dose (STD) adult head CT protocol in terms of quantitative and qualitative IQ. The signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of the white matter (WM) and gray matter (GM) and contrast-to-noise ratio (CNR) values in the LD groups were higher than the STD group. The differences were statistically significant. When the STD and the LD groups were compared qualitatively, no significant differences were found in overall quality. By selecting the appropriate level of IR 34%, radiation dose reduction in adult head CT can be achieved without compromising IQ.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The optimal dose reduction level using iterative reconstruction with prospective ECG-triggered coronary CTA using 256-slice MDCT.Eur J Radiol. 2012 Dec;81(12):3905-11. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2012.06.022. Epub 2012 Oct 1. Eur J Radiol. 2012. PMID: 23036786
-
Comparison of iterative model, hybrid iterative, and filtered back projection reconstruction techniques in low-dose brain CT: impact of thin-slice imaging.Neuroradiology. 2016 Mar;58(3):245-51. doi: 10.1007/s00234-015-1631-4. Epub 2015 Dec 29. Neuroradiology. 2016. PMID: 26715558
-
Sinogram affirmed iterative reconstruction in head CT: improvement of objective and subjective image quality with concomitant radiation dose reduction.Eur J Radiol. 2013 Sep;82(9):1431-5. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2013.03.011. Epub 2013 Apr 12. Eur J Radiol. 2013. PMID: 23587902 Clinical Trial.
-
Low radiation dose 256-MDCT angiography of the carotid arteries: effect of hybrid iterative reconstruction technique on noise, artifacts, and image quality.Eur J Radiol. 2013 Dec;82(12):2233-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2013.08.053. Epub 2013 Sep 12. Eur J Radiol. 2013. PMID: 24094643
-
256-MDCT for evaluation of urolithiasis: iterative reconstruction allows for a significant reduction of the applied radiation dose while maintaining high subjective and objective image quality.J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2014;58(3):283-90. doi: 10.1111/1754-9485.12159. Epub 2014 Mar 3. J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24581030 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Dose Reduction While Preserving Diagnostic Quality in Head CT: Advancing the Application of Iterative Reconstruction Using a Live Animal Model.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2019 Nov;40(11):1864-1870. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A6258. Epub 2019 Oct 10. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2019. PMID: 31601574 Free PMC article.
-
Comparisons of Hounsfield Unit Linearity between Images Reconstructed using an Adaptive Iterative Dose Reduction (AIDR) and a Filter Back-Projection (FBP) Techniques.J Biomed Phys Eng. 2020 Apr 1;10(2):215-224. doi: 10.31661/jbpe.v0i0.1912-1013. eCollection 2020 Apr. J Biomed Phys Eng. 2020. PMID: 32337189 Free PMC article.
-
Do Radiographic Assessments of Periodontal Bone Loss Improve with Deep Learning Methods for Enhanced Image Resolution?Sensors (Basel). 2021 Mar 12;21(6):2013. doi: 10.3390/s21062013. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33809165 Free PMC article.
-
Low-dose whole-body CT using deep learning image reconstruction: image quality and lesion detection.Br J Radiol. 2021 May 1;94(1121):20201329. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20201329. Epub 2021 Feb 22. Br J Radiol. 2021. PMID: 33571010 Free PMC article.
-
Ultra-low-dose hepatic computed tomography with a novel real-time deep learning-based noise reduction algorithm: a prospective cross-sectional analysis of image quality and lesion detection.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2025 Aug 1;15(8):7006-7018. doi: 10.21037/qims-2025-365. Epub 2025 Jul 24. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2025. PMID: 40785866 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hounsfield GH. Computerized transverse axial Scanning (tomography). I. Description of system. Br J Radiol. 1973;46(552):1016–22. - PubMed
-
- Ambrose J. Computerized transverse axial scanning (tomography): Part 2. Clinical application. Br J Radiol. 1973;46(552):1023–46. - PubMed
-
- Weber AL. History of head and neck radiology: past, present, and future. Radiology. 2001;218(1):15–24. - PubMed
-
- Mettler FA Jr, Bhargavan M, Faulkner K, et al. Radiologic and nuclear medicine studies in the United States and worldwide: frequency, radiation dose, and comparison with other radiation sources–1950‐2007. Radiology. 2009;253(2):520–31. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

