Synaptic microRNAs Coordinately Regulate Synaptic mRNAs: Perturbation by Chronic Alcohol Consumption
- PMID: 26105134
- PMCID: PMC5130129
- DOI: 10.1038/npp.2015.179
Synaptic microRNAs Coordinately Regulate Synaptic mRNAs: Perturbation by Chronic Alcohol Consumption
Abstract
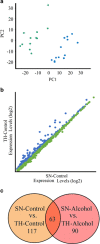
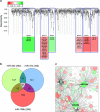
Local translation of mRNAs in the synapse has a major role in synaptic structure and function. Chronic alcohol use causes persistent changes in synaptic mRNA expression, possibly mediated by microRNAs localized in the synapse. We profiled the transcriptome of synaptoneurosomes (SN) obtained from the amygdala of mice that consumed 20% ethanol (alcohol) in a 30-day continuous two-bottle choice test to identify the microRNAs that target alcohol-induced mRNAs. SN are membrane vesicles containing pre- and post-synaptic compartments of neurons and astroglia and are a unique model for studying the synaptic transcriptome. We previously showed that chronic alcohol regulates mRNA expression in a coordinated manner. Here, we examine microRNAs and mRNAs from the same samples to define alcohol-responsive synaptic microRNAs and their predicted interactions with targeted mRNAs. The aim of the study was to identify the microRNA-mRNA synaptic interactions that are altered by alcohol. This was accomplished by comparing the effect of alcohol in SN and total homogenate preparations from the same samples. We used a combination of unbiased bioinformatic methods (differential expression, correlation, co-expression, microRNA-mRNA target prediction, co-targeting, and cell type-specific analyses) to identify key alcohol-sensitive microRNAs. Prediction analysis showed that a subset of alcohol-responsive microRNAs was predicted to target many alcohol-responsive mRNAs, providing a bidirectional analysis for identifying microRNA-mRNA interactions. We found microRNAs and mRNAs with overlapping patterns of expression that correlated with alcohol consumption. Cell type-specific analysis revealed that a significant number of alcohol-responsive mRNAs and microRNAs were unique to glutamate neurons and were predicted to target each other. Chronic alcohol consumption appears to perturb the coordinated microRNA regulation of mRNAs in SN, a mechanism that may explain the aberrations in synaptic plasticity affecting the alcoholic brain.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Silencing synaptic MicroRNA-411 reduces voluntary alcohol consumption in mice.Addict Biol. 2019 Jul;24(4):604-616. doi: 10.1111/adb.12625. Epub 2018 Apr 17. Addict Biol. 2019. PMID: 29665166 Free PMC article.
-
miRNA and mRNA expression profiling in rat brain following alcohol dependence and withdrawal.Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2017 Feb 28;63(2):49-56. doi: 10.14715/cmb/2017.63.2.7. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2017. PMID: 28364783
-
Coordinated dysregulation of mRNAs and microRNAs in the rat medial prefrontal cortex following a history of alcohol dependence.Pharmacogenomics J. 2013 Jun;13(3):286-96. doi: 10.1038/tpj.2012.17. Epub 2012 May 22. Pharmacogenomics J. 2013. PMID: 22614244 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptic adaptations by alcohol and drugs of abuse: changes in microRNA expression and mRNA regulation.Front Mol Neurosci. 2014 Dec 16;7:85. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2014.00085. eCollection 2014. Front Mol Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25565954 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Maternal alcohol consumption and altered miRNAs in the developing fetus: Context and future perspectives.J Appl Toxicol. 2018 Jan;38(1):100-107. doi: 10.1002/jat.3504. Epub 2017 Jul 5. J Appl Toxicol. 2018. PMID: 28677831 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular mechanisms underlying alcohol-drinking behaviours.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2016 Sep;17(9):576-91. doi: 10.1038/nrn.2016.85. Epub 2016 Jul 21. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27444358 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging roles for ncRNAs in alcohol use disorders.Alcohol. 2017 May;60:31-39. doi: 10.1016/j.alcohol.2017.01.004. Epub 2017 Apr 15. Alcohol. 2017. PMID: 28438526 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miRNAs and Substances Abuse: Clinical and Forensic Pathological Implications: A Systematic Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 4;24(23):17122. doi: 10.3390/ijms242317122. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38069445 Free PMC article.
-
Deep sequencing and miRNA profiles in alcohol-induced neuroinflammation and the TLR4 response in mice cerebral cortex.Sci Rep. 2018 Oct 29;8(1):15913. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-34277-y. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30374194 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Adult Neurogenesis by Non-coding RNAs: Implications for Substance Use Disorders.Front Neurosci. 2018 Nov 22;12:849. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2018.00849. eCollection 2018. Front Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30524229 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

