Dissociating Motivational From Physiological Withdrawal in Alcohol Dependence: Role of Central Amygdala κ-Opioid Receptors
- PMID: 26105136
- PMCID: PMC5130131
- DOI: 10.1038/npp.2015.183
Dissociating Motivational From Physiological Withdrawal in Alcohol Dependence: Role of Central Amygdala κ-Opioid Receptors
Abstract
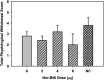
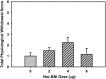
Chronic intermittent alcohol vapor exposure leads to increased dynorphin (DYN) A-like peptide expression and heightened kappa-opioid receptor (KOR) signaling in the central nucleus of the amygdala (CeA) and these neuroadaptive responses differentiate alcohol-dependent from non-dependent phenotypes. Important for therapeutic development efforts is understanding the nature of the stimulus that drives dependence-like phenotypes such as escalated alcohol self-administration. Accordingly, the present study examined the impact of intra-CeA KOR antagonism on escalated operant alcohol self-administration and physiological withdrawal symptoms during acute withdrawal and protracted abstinence in rats previously exposed to chronic intermittent alcohol vapor. Following operant training, rats were implanted with intra-CeA guide cannula and exposed to long-term intermittent alcohol vapor exposure that resulted in escalated alcohol self-administration and elevated physiological withdrawal signs during acute withdrawal. Animals received intra-CeA infusions of the KOR antagonist nor-binaltorphimine (nor-BNI; 0, 2, 4, or 6 μg) prior to operant alcohol self-administration sessions and physiological withdrawal assessment during acute withdrawal and protracted abstinence. The results indicated that site-specific KOR antagonism in the CeA ameliorated escalated alcohol self-administration during both acute withdrawal and protracted abstinence test sessions, whereas KOR antagonism had no effect on physiological withdrawal scores at either time point. These results dissociate escalated alcohol self-administration from physiological withdrawal symptoms in relation to KOR signaling in the CeA and help clarify the nature of the stimulus that drives escalated alcohol self-administration during acute withdrawal and protracted abstinence.
Figures



References
-
- Alheid GF, Heimer L (1988). New perspectives in basal forebrain organization of special relevance for neuropsychiatric disorders: the striatopallidal, amygdaloid, and corticopetal components of substantia innominata. Neuroscience 27: 1–39. - PubMed
-
- Bazov I, Kononenko O, Watanabe H, Kuntic V, Sarkisyan D, Taqi MM et al (2013). The endogenous opioid system in human alcoholics: molecular adaptations in brain areas involved in cognitive control of addiction. Addict Biol 18: 161–169. - PubMed
-
- Berthoud HR (2002). Multiple neural systems controlling food intake and body weight. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 26: 393–428. - PubMed
-
- Broadbear JH, Negus SS, Butelman ER, de Costa BR, Woods JH (1994). Differential effects of systemically administered nor-binaltorphimine (nor-BNI) on kappa-opioid agonists in the mouse writhing assay. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 115: 311–319. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

