Breast-feeding and complementary feeding practices in the first 6 months of life among Norwegian-Somali and Norwegian-Iraqi infants: the InnBaKost survey
- PMID: 26105703
- PMCID: PMC10271049
- DOI: 10.1017/S1368980015001962
Breast-feeding and complementary feeding practices in the first 6 months of life among Norwegian-Somali and Norwegian-Iraqi infants: the InnBaKost survey
Abstract
Objective: To examine breast-feeding and complementary feeding practices during the first 6 months of life among Norwegian infants of Somali and Iraqi family origin.
Design: A cross-sectional survey was performed during March 2013-February 2014. Data were collected using a semi-quantitative FFQ adapted from the second Norwegian national dietary survey among infants in 2006-2007.
Setting: Somali-born and Iraqi-born mothers living in eastern Norway were invited to participate.
Subjects: One hundred and seven mothers/infants of Somali origin and eighty mothers/infants of Iraqi origin participated.
Results: Breast-feeding was almost universally initiated after birth. Only 7 % of Norwegian-Somali and 10 % of Norwegian-Iraqi infants were exclusively breast-fed at 4 months of age. By 1 month of age, water had been introduced to 30 % of Norwegian-Somali and 26 % of Norwegian-Iraqi infants, and infant formula to 44 % and 34 %, respectively. Fifty-four per cent of Norwegian-Somali and 68 % of Norwegian-Iraqi infants had been introduced to solid or semi-solid foods at 4 months of age. Breast-feeding at 6 months of age was more common among Norwegian-Somali infants (79 %) compared with Norwegian-Iraqi infants (58 %; P=0·001). Multivariate analyses indicated no significant factors associated with exclusive breast-feeding at 3·5 months of age. Factors positively associated with breast-feeding at 6 months were country of origin (Somalia) and parity (>2).
Conclusions: Breast-feeding initiation was common among Iraqi-born and Somali-born mothers, but the exclusive breast-feeding period was shorter than recommended in both groups. The study suggests that there is a need for new culture-specific approaches to support exclusive breast-feeding and complementary feeding practices among foreign-born mothers living in Norway.
Keywords: Breast-feeding; Exclusive breast-feeding; Immigrants; Infant feeding.
Figures
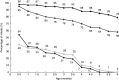
 ) and Norwegian-Iraqi (
) and Norwegian-Iraqi ( ) infants and breast-feeding among Norwegian-Somali (
) infants and breast-feeding among Norwegian-Somali ( ) and Norwegian-Iraqi (
) and Norwegian-Iraqi ( ) infants during the first 6 months of life (Somali n 107; Iraqi n 80); InnBaKost survey, March 2013–February 2014
) infants during the first 6 months of life (Somali n 107; Iraqi n 80); InnBaKost survey, March 2013–February 2014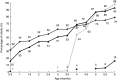
 ), water (
), water ( ), sweetened drinks/fruit juices (
), sweetened drinks/fruit juices ( ) and solid and/or semi-solid foods (
) and solid and/or semi-solid foods ( ) to Norwegian-Somali infants during the first 6 months of life (n 107); InnBaKost survey, March 2013–February 2014
) to Norwegian-Somali infants during the first 6 months of life (n 107); InnBaKost survey, March 2013–February 2014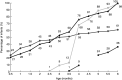
 ), water (
), water ( ), sweetened drinks/fruit juices (
), sweetened drinks/fruit juices ( ) and solid and/or semi-solid foods (
) and solid and/or semi-solid foods ( ) to Norwegian-Iraqi infants during the first 6 months of life (n 80); InnBaKost survey, March 2013–February 2014
) to Norwegian-Iraqi infants during the first 6 months of life (n 80); InnBaKost survey, March 2013–February 2014References
-
- Butte NF, Lopez-Alarcon MG & Garza C (2002) Nutrient Adequacy of Exclusive Breastfeeding for the Term Infant During the First Six Months of Life. Geneva: WHO.
-
- World Health Organization (2013) Long-Term Effects of Breastfeeding – A Systematic Review. Geneva: WHO.
-
- Moss BG & Yeaton WH (2014) Early childhood healthy and obese weight status: potentially protective benefits of breastfeeding and delaying solid foods. Matern Child Health J 18, 1224–1232. - PubMed
-
- Owen CG, Martin RM, Whincup PH et al.. (2005) Effect of infant feeding on the risk of obesity across the life course: a quantitative review of published evidence. Pediatrics 115, 1367–1377. - PubMed

