Effect of single point mutations in a form of systemic amyloidosis
- PMID: 26105812
- PMCID: PMC4570539
- DOI: 10.1002/pro.2730
Effect of single point mutations in a form of systemic amyloidosis
Abstract
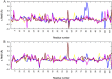
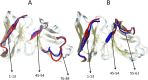
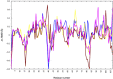
Amyloid deposits of light-chain proteins are associated with the most common form of systemic amyloidosis. We have studied the effects of single point mutations on amyloid formation of these proteins using explicit solvent model molecular dynamics simulations. For this purpose, we compare the stability of the wild-type immunoglobulin light-chain protein REI in its native and amyloid forms with that of four mutants: R61N, G68D, D82I, and A84T. We argue that the experimentally observed differences in the propensity for amyloid formation result from two effects. First, the mutant dimers have a lower stability than the wild-type dimer due to increase exposure of certain hydrophobic residues. The second effect is a shift in equilibrium between monomers with amyloid-like structure and such with native structures. Hence, when developing drugs against light-chain associated systemic amyloidosis, one should look for components that either stabilize the dimer by binding to the dimer interface or reduce for the monomers the probability of the amyloid form.
Keywords: aggregation; light-chain proteins; molecular dynamics; systemic amyloidosis.
© 2015 The Protein Society.
Figures

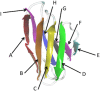
Similar articles
-
Immunoglobulin light chain amyloid aggregation.Chem Commun (Camb). 2018 Sep 20;54(76):10664-10674. doi: 10.1039/c8cc04396e. Chem Commun (Camb). 2018. PMID: 30087961 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunoglobulin kappa light chain and its amyloidogenic mutants: a molecular dynamics study.Proteins. 2004 Apr 1;55(1):11-21. doi: 10.1002/prot.10606. Proteins. 2004. PMID: 14997536
-
Differential effects on light chain amyloid formation depend on mutations and type of glycosaminoglycans.J Biol Chem. 2015 Feb 20;290(8):4953-4965. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.615401. Epub 2014 Dec 23. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25538238 Free PMC article.
-
Decreased amyloidogenicity caused by mutational modulation of surface properties of the immunoglobulin light chain BRE variable domain.Biochemistry. 2014 Aug 12;53(31):5162-73. doi: 10.1021/bi5007892. Epub 2014 Aug 4. Biochemistry. 2014. PMID: 25062800
-
Dynamic protein structures in normal function and pathologic misfolding in systemic amyloidosis.Biophys Chem. 2022 Jan;280:106699. doi: 10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106699. Epub 2021 Oct 14. Biophys Chem. 2022. PMID: 34773861 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Understanding Mesangial Pathobiology in AL-Amyloidosis and Monoclonal Ig Light Chain Deposition Disease.Kidney Int Rep. 2020 Jul 21;5(11):1870-1893. doi: 10.1016/j.ekir.2020.07.013. eCollection 2020 Nov. Kidney Int Rep. 2020. PMID: 33163710 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure and energetic basis of overrepresented λ light chain in systemic light chain amyloidosis patients.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2018 Jun;1864(6 Pt B):2294-2303. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2017.12.009. Epub 2017 Dec 12. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2018. PMID: 29241665 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Developments and Applications of the MMPBSA Method.Front Mol Biosci. 2018 Jan 10;4:87. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2017.00087. eCollection 2017. Front Mol Biosci. 2018. PMID: 29367919 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phase 2 trial of daily, oral epigallocatechin gallate in patients with light-chain amyloidosis.Int J Hematol. 2017 Mar;105(3):295-308. doi: 10.1007/s12185-016-2112-1. Epub 2016 Nov 4. Int J Hematol. 2017. PMID: 27815860 Clinical Trial.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

