Telescopic Overdenture and Implant Supported Fixed Partial Denture: A Pragmatic Treatment Approach
- PMID: 26106491
- PMCID: PMC4461731
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/392397
Telescopic Overdenture and Implant Supported Fixed Partial Denture: A Pragmatic Treatment Approach
Abstract
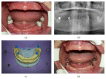
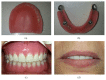
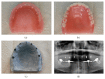
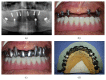
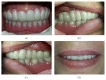
This case report presents a patient who had been rehabilitated with a telescopic overdenture and implant supported fixed partial denture (ISFPD). The treatment process was as follows: (1) fabricating telescopic crowns and overdenture prosthesis for the lower jaw and a temporary complete denture for the upper jaw, (2) using the temporary denture as diagnostic and surgical guide to optimize dental implant placement, and (3) fabricating ISFPD for the upper jaw. Using the patient's existing or temporary denture not only serves as an alternative surgical guide to calibrate the dental implant locations but also helps to finish the restoration at desired dimension, size, and anatomic form.
Figures
References
-
- Kwon H. B., Roh Y. H., Lee S. H. The comparison of initial retentive force in different double crown systems. Journal of Korean Academy of Prosthodontics. 2006;44(6):677–682.
-
- Batenburg R. H. K., Meijer H. J. A., Raghoebar G. M., Vissink A. Treatment concept for mandibular overdentures supported by endoosseous implants: a literature review. International Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Implants. 1998;13(4):539–545. - PubMed
-
- Turk Y., Işık G. The treatment of an upper partial edentulous patient with telescopic crown retained removable partial denture: a case report. Istanbul Üniversitesi Dis Hekimligi Fakültesi Dergisi. 2008;12:41–44.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

