Brain structural, functional, and cognitive correlates of recent versus remote autobiographical memories in amnestic Mild Cognitive Impairment
- PMID: 26106572
- PMCID: PMC4474362
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nicl.2015.05.010
Brain structural, functional, and cognitive correlates of recent versus remote autobiographical memories in amnestic Mild Cognitive Impairment
Abstract
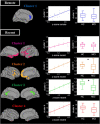
Deficits in autobiographical memory appear earlier for recent than for remote life periods over the course of Alzheimer's disease (AD). The present study aims to further our understanding of this graded effect by investigating the cognitive and neural substrates of recent versus remote autobiographical memories in patients with amnestic Mild Cognitive Impairment (aMCI) thanks to an autobiographical fluency task. 20 aMCI patients and 25 Healthy elderly Controls (HC) underwent neuropsychological tests assessing remote (20-to-30 years old) and recent (the ten last years) autobiographical memory as well as episodic and semantic memory, executive function and global cognition. All patients also had a structural MRI and an FDG-PET scan. Correlations were assessed between each autobiographical memory score and the other tests as well as grey matter volume and metabolism. Within the aMCI, performances for the remote period correlated with personal semantic memory and episodic memory retrieval whereas performances for the recent period only correlated with episodic memory retrieval. Neuroimaging analyses revealed significant correlations between performances for the remote period and temporal pole and temporo-parietal cortex volumes and anterior cingulate gyrus metabolism, while performances for the recent period correlated with hippocampal volume and posterior cingulate, medial prefrontal and hippocampus metabolism. The brain regions related with the retrieval of events from the recent period showed greater atrophy/hypometabolism in aMCI patients compared to HC than those involved in remote memories. Recall of recent memories essentially relies on episodic memory processes and brain network while remote memories also involve other processes such as semantic memory. This is consistent with the semanticization of memories with time and may explain the better resistance of remote memory in AD.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; Autobiographical memory; FDG-PET; MRI; Mild Cognitive Impairment; VBM.
Figures


References
-
- Baddeley Alan, Wilson B.A. Amnesia, autobiographical memory and confabulation. In: Rubin D., editor. Cambridge; Cambridge University Press: 1986. pp. 225–252. (Autobiographical Memory).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

