Glypican-1 identifies cancer exosomes and detects early pancreatic cancer
- PMID: 26106858
- PMCID: PMC4825698
- DOI: 10.1038/nature14581
Glypican-1 identifies cancer exosomes and detects early pancreatic cancer
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Glypican-1 identifies cancer exosomes and detects early pancreatic cancer.Nature. 2022 Oct;610(7932):E15-E17. doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-05062-9. Nature. 2022. PMID: 36198804 No abstract available.
Abstract
Exosomes are lipid-bilayer-enclosed extracellular vesicles that contain proteins and nucleic acids. They are secreted by all cells and circulate in the blood. Specific detection and isolation of cancer-cell-derived exosomes in the circulation is currently lacking. Using mass spectrometry analyses, we identify a cell surface proteoglycan, glypican-1 (GPC1), specifically enriched on cancer-cell-derived exosomes. GPC1(+) circulating exosomes (crExos) were monitored and isolated using flow cytometry from the serum of patients and mice with cancer. GPC1(+) crExos were detected in the serum of patients with pancreatic cancer with absolute specificity and sensitivity, distinguishing healthy subjects and patients with a benign pancreatic disease from patients with early- and late-stage pancreatic cancer. Levels of GPC1(+) crExos correlate with tumour burden and the survival of pre- and post-surgical patients. GPC1(+) crExos from patients and from mice with spontaneous pancreatic tumours carry specific KRAS mutations, and reliably detect pancreatic intraepithelial lesions in mice despite negative signals by magnetic resonance imaging. GPC1(+) crExos may serve as a potential non-invasive diagnostic and screening tool to detect early stages of pancreatic cancer to facilitate possible curative surgical therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
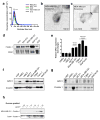
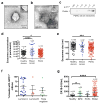
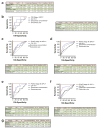
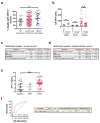



Comment in
-
Cancer: Diagnosis by extracellular vesicles.Nature. 2015 Jul 9;523(7559):161-2. doi: 10.1038/nature14626. Epub 2015 Jun 24. Nature. 2015. PMID: 26106856 No abstract available.
-
Biomarkers: The challenge to find biomarkers for the early detection of pancreatic cancer.Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015 Aug;12(8):427. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2015.118. Epub 2015 Jul 14. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015. PMID: 26170217 No abstract available.
-
Diagnosis: Fishing for exosomes.Nat Rev Cancer. 2015 Aug;15(8):453. doi: 10.1038/nrc3990. Nat Rev Cancer. 2015. PMID: 26205334 No abstract available.
-
Glypican-1 as a highly sensitive and specific pancreatic cancer biomarker.Clin Chem Lab Med. 2016 Jan;54(1):e1-2. doi: 10.1515/cclm-2015-0773. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2016. PMID: 26389634 No abstract available.
-
Glypican-1 exosomes: do they initiate a new era for early pancreatic cancer diagnosis?Transl Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016 Mar 16;1:8. doi: 10.21037/tgh.2016.01.07. eCollection 2016. Transl Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016. PMID: 28164166 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P30 CA016672/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA151925/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30-CA016672/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA16672/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30CA016672/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50-CA094056/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- DK 081576/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA155370/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 5U24-CA126577/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-151925/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-155370/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30CA16672/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA094056/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA126577/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK081576/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

