Cranial Morphology of the Brachystelechid 'Microsaur' Quasicaecilia texana Carroll Provides New Insights into the Diversity and Evolution of Braincase Morphology in Recumbirostran 'Microsaurs'
- PMID: 26107260
- PMCID: PMC4479878
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0130359
Cranial Morphology of the Brachystelechid 'Microsaur' Quasicaecilia texana Carroll Provides New Insights into the Diversity and Evolution of Braincase Morphology in Recumbirostran 'Microsaurs'
Abstract
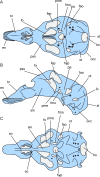
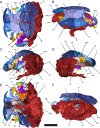
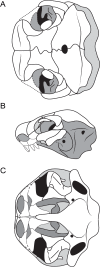
Recumbirostran 'microsaurs,' a group of early tetrapods from the Late Carboniferous and Early Permian, are the earliest known example of adaptation to head-first burrowing in the tetrapod fossil record. However, understanding of the diversity of fossorial adaptation within the Recumbirostra has been hindered by poor anatomical knowledge of the more divergent forms within the group. Here we report the results of μCT study of Quasicaecilia texana, a poorly-known recumbirostran with a unique, broad, shovel-like snout. The organization of the skull roof and braincase of Quasicaecilia is found to be more in line with that of other recumbirostrans than previously described, despite differences in overall shape. The braincase is found to be broadly comparable to Carrolla craddocki, with a large presphenoid that encompasses much of the interorbital septum and the columella ethmoidalis, and a single compound ossification encompassing the sphenoid, otic, and occipital regions. The recumbirostran braincase conserves general structure and topology of braincase regions and cranial nerve foramina, but it is highly variable in the number of ossifications and their extent, likely associated with the reliance on braincase ossifications to resist compression during sediment compaction and mechanical manipulation by epaxial and hypaxial musculature. Expansion of the deep ventral neck musculature in Quasicaecilia, autapomorphic among recumbirostrans, may reflect unique biomechanical function, and underscores the importance of future attention to the role of the cervical musculature in contextualizing the origin and evolution of fossoriality in recumbirostrans.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Anderson JS (2007) Incorporating ontogeny into the matrix: a phylogenetic evaluation of developmental evidence for the origin of modern amphibians In: Anderson JS, Sues H-D, editors. Major Transitions in Vertebrate Evolution. Indiana: Indiana University Press; pp. 182–227.
-
- Anderson JS (2001) The phylogenetic trunk: maximal inclusion of taxa with missing data in an analysis of the Lepospondyli (Vertebrata, Tetrapoda). Syst Biol 50:170–193. - PubMed
-
- Vallin G, Laurin M (2004) Cranial morphology and affinities of Microbrachis, and a reappraisal of the phylogeny and lifestyle of the first amphibians. J Vertebr Paleontol 24: 56–72.
-
- Marjanović D, Laurin M (2008) A reevaluation of the evidence supporting an unorthodox hypothesis on the origin of extant amphibians. Contrib Zool 77: 149–199.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

