International Laboratory Comparison of Influenza Microneutralization Assays for A(H1N1)pdm09, A(H3N2), and A(H5N1) Influenza Viruses by CONSISE
- PMID: 26108286
- PMCID: PMC4519725
- DOI: 10.1128/CVI.00278-15
International Laboratory Comparison of Influenza Microneutralization Assays for A(H1N1)pdm09, A(H3N2), and A(H5N1) Influenza Viruses by CONSISE
Abstract
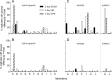
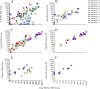
The microneutralization assay is commonly used to detect antibodies to influenza virus, and multiple protocols are used worldwide. These protocols differ in the incubation time of the assay as well as in the order of specific steps, and even within protocols there are often further adjustments in individual laboratories. The impact these protocol variations have on influenza serology data is unclear. Thus, a laboratory comparison of the 2-day enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and 3-day hemagglutination (HA) microneutralization (MN) protocols, using A(H1N1)pdm09, A(H3N2), and A(H5N1) viruses, was performed by the CONSISE Laboratory Working Group. Individual laboratories performed both assay protocols, on multiple occasions, using different serum panels. Thirteen laboratories from around the world participated. Within each laboratory, serum sample titers for the different assay protocols were compared between assays to determine the sensitivity of each assay and were compared between replicates to assess the reproducibility of each protocol for each laboratory. There was good correlation of the results obtained using the two assay protocols in most laboratories, indicating that these assays may be interchangeable for detecting antibodies to the influenza A viruses included in this study. Importantly, participating laboratories have aligned their methodologies to the CONSISE consensus 2-day ELISA and 3-day HA MN assay protocols to enable better correlation of these assays in the future.
Copyright © 2015, Laurie et al.
Figures
References
-
- Chen MI, Barr IG, Koh GCH, Lee VJ, Lee CPS, Shaw R, Lin C, Yap J, Cook AR, Tan BH, Loh JP, Barkham T, Chow VTK, Lin RTP, Leo YS. 2010. Serological response in RT-PCR confirmed H1N1-2009 influenza A by hemagglutination inhibition and virus neutralization assays: an observational study. PLoS One 5:e12474. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0012474. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Veguilla V, Hancock K, Schiffer J, Gargiullo P, Lu X, Aranio D, Branch A, Dong L, Holiday C, Liu F, Steward-Clark E, Sun H, Tsang B, Wang D, Whaley M, Bai Y, Cronin L, Browning P, Dababneh H, Noland H, Thomas L, Foster L, Quinn CP, Soroka SD, Katz JM. 2011. Sensitivity and specificity of serologic assays for the detection of human infection with 2009 pandemic H1N1 virus in U.S. populations. J Clin Microbiol 49:2210–2215. doi:10.1128/JCM.00229-11. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Laurie KL, Huston P, Riley S, Katz JM, Willison DJ, Tam JS, Mounts AW, Hoschler K, Miller E, Vandemaele K, Broberg E, Van Kerkhove MD, Nicoll A. 30 April 2012. Influenza serological studies to inform public health action: best practices to optimise timing, quality and reporting. Influenza Other Respir Viruses doi:10.1111/j.1750-2659.2012.0370a.x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

