Effectiveness, safety and costs of orphan drugs: an evidence-based review
- PMID: 26109112
- PMCID: PMC4480037
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2014-007199
Effectiveness, safety and costs of orphan drugs: an evidence-based review
Erratum in
-
Correction.BMJ Open. 2015 Oct 26;5(10):e007199corr1. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2014-007199corr1. BMJ Open. 2015. PMID: 26503381 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Introduction: Several orphan drugs have been approved by the European Medicines Agency (EMA) over the past two decades. However, the drugs are expensive, and in some instances, the evidence for effectiveness is not convincing at the time of regulatory approval. Our objective was to evaluate the clinical effectiveness of orphan drugs that have been granted marketing licenses in Europe, determine the annual costs of each drug, compare the costs of branded orphan drugs against their generic equivalents, and explore any relationships between orphan drug disease prevalence and annual costs.
Methods: We searched the EMA database to identify orphan drugs granted marketing authorisation up to April 2014. Electronic searches were also conducted in PubMed, EMBASE and Google Scholar, to assess data on effectiveness, safety and annual costs. 2 reviewers independently evaluated the levels and quality of evidence, and extracted data.
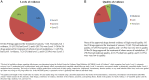
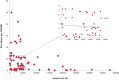
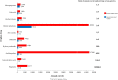
Results: We identified 74 orphan drugs, with 54 (73%) demonstrating moderate quality of evidence. 85% showed significant clinical effects, but serious adverse events were reported in 86.5%. Their annual costs were between £726 and £378,000. There was a significant inverse relationship between disease prevalence and annual costs (p = 0.01); this was largely due to the influence of the ultra-orphan diseases. We could not determine whether the balance between effectiveness and safety influenced annual costs. For 10 drugs where generic alternatives were available, the branded drugs were 1.4 to 82,000 times more expensive.
Conclusions: The available evidence suggests that there is inconsistency in the quality of evidence of approved orphan drugs, and there is no clear mechanism for determining their prices. In some cases, far cheaper generic agents appear to be available. A more robust, transparent and standard mechanism for determining annual costs is imperative.
Keywords: GENERAL MEDICINE (see Internal Medicine); ORPHAN DRUGS; PRIMARY CARE.
Published by the BMJ Publishing Group Limited. For permission to use (where not already granted under a licence) please go to http://group.bmj.com/group/rights-licensing/permissions.
Figures


References
-
- European Medicines Agency (EMA). Orphan drugs and rare diseases at a glance. http://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/Other/2010/01/WC500...
-
- National Institute for Clinical Excellence. NICE citizens council report ultra orphan drugs. London: NICE, 2004. http://www.nice.org.uk/proxy/?sourceUrl=http://www.nice.org.uk/niceMedia... (accessed 7 May 2015). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
