Retinoic Acid Signaling Coordinates Macrophage-Dependent Injury and Repair after AKI
- PMID: 26109319
- PMCID: PMC4731115
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2014111108
Retinoic Acid Signaling Coordinates Macrophage-Dependent Injury and Repair after AKI
Abstract
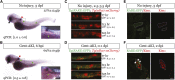
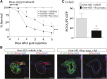
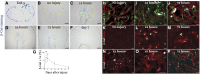
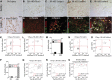
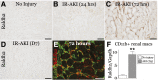
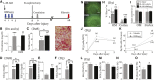
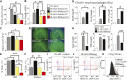
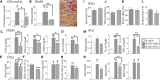
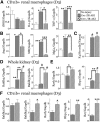
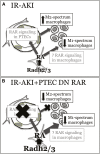
Retinoic acid (RA) has been used therapeutically to reduce injury and fibrosis in models of AKI, but little is known about the regulation of this pathway and what role it has in regulating injury and repair after AKI. In these studies, we show that RA signaling is activated in mouse and zebrafish models of AKI, and that these responses limit the extent of injury and promote normal repair. These effects were mediated through a novel mechanism by which RA signaling coordinated the dynamic equilibrium of inflammatory M1 spectrum versus alternatively activated M2 spectrum macrophages. Our data suggest that locally synthesized RA represses proinflammatory macrophages, thereby reducing macrophage-dependent injury post-AKI, and activates RA signaling in injured tubular epithelium, which in turn promotes alternatively activated M2 spectrum macrophages. Because RA signaling has an essential role in kidney development but is repressed in the adult, these findings provide evidence of an embryonic signaling pathway that is reactivated after AKI and involved in reducing injury and enhancing repair.
Keywords: acute renal failure; macrophages; renal injury; renal proximal tubule cell; signaling; tubular epithelium.
Copyright © 2016 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures
References
-
- Batourina E, Gim S, Bello N, Shy M, Clagett-Dame M, Srinivas S, Costantini F, Mendelsohn C: Vitamin A controls epithelial/mesenchymal interactions through Ret expression. Nat Genet 27: 74–78, 2001 - PubMed
-
- Maden M: Retinoic acid and limb regeneration—a personal view. Int J Dev Biol 46: 883–886, 2002 - PubMed
-
- Maden M: The effect of vitamin A on the regenerating axolotl limb. J Embryol Exp Morphol 77: 273–295, 1983 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- T35 DK007383/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK51265/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- RC4 DK090770/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 2R01-HD053287/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK079307/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK95785/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK069403/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 1P30-DK079307/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DK038226/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK095785/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL093057/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 1RC4-DK090770/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 1R01-HL093057/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 2R01-DK069403/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30-DK079307/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK051265/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK38226/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK056942/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD053287/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- 1RC-4DK090770/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK62794/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK062794/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- F30 DK101143/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

