Apocynin Attenuates Cardiac Injury in Type 4 Cardiorenal Syndrome via Suppressing Cardiac Fibroblast Growth Factor-2 With Oxidative Stress Inhibition
- PMID: 26109504
- PMCID: PMC4608061
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.114.001598
Apocynin Attenuates Cardiac Injury in Type 4 Cardiorenal Syndrome via Suppressing Cardiac Fibroblast Growth Factor-2 With Oxidative Stress Inhibition
Abstract
Background: Type 4 cardiorenal syndrome (CRS) refers to the cardiac injury induced by chronic kidney disease. We aimed to assess oxidative stress and cardiac injury in patients with type 4 CRS, determine whether the antioxidant apocynin attenuated cardiac injury in rats with type 4 CRS, and explore potential mechanisms.
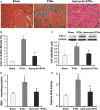
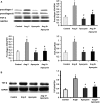
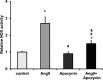
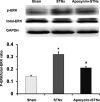
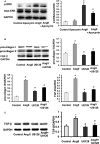
Methods and results: A cross-sectional study was conducted among patients with type 4 CRS (n=17) and controls (n=16). Compared with controls, patients with type 4 CRS showed elevated oxidative stress, which was significantly correlated with cardiac hypertrophy and decreased ejection fraction. In vivo study, male Sprague-Dawley rats underwent 5/6 subtotal nephrectomy and sham surgery, followed with apocynin or vehicle treatment for 8 weeks. Eight weeks after surgery, the 5/6 subtotal nephrectomy rats mimicked type 4 CRS, showing increased serum creatinine, cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis, and decreased ejection fraction compared with sham-operated animals. Cardiac malondialdehyde, NADPH oxidase activity, fibroblast growth factor-2, and extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2) phosphorylation increased significantly in the 5/6 subtotal nephrectomy rats. These changes were significantly attenuated by apocynin. In vitro study showed that apocynin reduced angiotensin II-induced NADPH oxidase-dependent oxidative stress, upregulation of fibroblast growth factor-2 and fibrosis biomarkers, and ERK1/2 phosphorylation in cardiac fibroblasts. Importantly, the ERK1/2 inhibitor U0126 reduced the upregulation of fibroblast growth factor-2 and fibrosis biomarkers in angiotensin II-treated fibroblasts.
Conclusions: Oxidative stress is a candidate mediator for type 4 CRS. Apocynin attenuated cardiac injury in type 4 CRS rats via inhibiting NADPH oxidase-dependent oxidative stress-activated ERK1/2 pathway and subsequent fibroblast growth factor-2 upregulation. Our study added evidence to the beneficial effect of apocynin in type 4 CRS.
Keywords: cardiac remodeling; cardiorenal syndrome; extracellular signal‐regulated kinase 1/2; fibroblast growth factor; pharmacology.
© 2015 The Authors. Published on behalf of the American Heart Association, Inc., by Wiley Blackwell.
Figures


References
-
- Ronco C, Haapio M, House AA, Anavekar N, Bellomo R. Cardiorenal syndrome. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008;52:1527–1539. - PubMed
-
- Tumlin JA, Costanzo MR, Chawla LS, Herzog CA, Kellum JA, McCullough PA, Ronco C. Cardiorenal syndrome type 4: insights on clinical presentation and pathophysiology from the eleventh consensus conference of the Acute Dialysis Quality Initiative (ADQI) Contrib Nephrol. 2013;182:158–173. - PubMed
-
- Bello AK, Nwankwo E, El Nahas AM. Prevention of chronic kidney disease: a global challenge. Kidney Int Suppl. 2005;98:S11–S17. - PubMed
-
- Jha V, Garcia-Garcia G, Iseki K, Li Z, Naicker S, Plattner B, Saran R, Wang AY, Yang CW. Chronic kidney disease: global dimension and perspectives. Lancet. 2013;382:260–272. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

