Increased Systemic and Plaque Inflammation in ABCA1 Mutation Carriers With Attenuation by Statins
- PMID: 26109739
- PMCID: PMC4484788
- DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.114.304959
Increased Systemic and Plaque Inflammation in ABCA1 Mutation Carriers With Attenuation by Statins
Abstract
Objective: We previously demonstrated that subjects with functional ATP-binding cassette (ABC) A1 mutations have increased atherosclerosis, which has been attributed to the role of ABCA1 in reverse cholesterol transport. More recently, a proinflammatory effect of Abca1 deficiency was shown in mice, potentially contributing to atherogenesis. In this study, we investigated whether ABCA1 deficiency was associated with proinflammatory changes in humans.
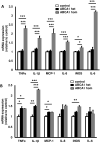
Approach and results: Thirty-one heterozygous, 5 homozygous ABCA1 mutation carriers, and 21 matched controls were studied. (18)Fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography with computed tomographic scanning was performed in a subset of carriers and controls to assess arterial wall inflammation (target:background ratio). Heterozygous ABCA1 mutation carriers had a 20% higher target:background ratio than in controls (target:background ratio; P=0.008). In carriers using statins (n=7), target:background ratio was 21% reduced than in nonstatin users (n=7; P=0.03). We then measured plasma cytokine levels. Tumor necrosis factor α, monocyte chemoattractant protein-1, and interleukin-6 levels were increased in heterozygous and homozygous ABCA1 mutation carriers. We isolated monocytes from carriers and controls and measured inflammatory gene expression. Only TNFα mRNA was increased in monocytes from heterozygous ABCA1 mutation carriers. Additional studies in THP-1 macrophages showed that both ABCA1 deficiency and lipoprotein-deficient plasma from ABCA1 mutation carriers increased inflammatory gene expression.
Conclusions: Our data suggest a proinflammatory state in ABCA1 mutation carriers as reflected by an increased positron emission tomography-MRI signal in nonstatin using subjects, and increased circulating cytokines. The increased inflammation in ABCA1 mutation carriers seems to be attenuated by statins.
Keywords: ABCA1; HDL; cytokines; dyslipidemia; genetics; lipids; positron-emission tomography.
© 2015 American Heart Association, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Comment in
-
ABCA1 and Inflammation: From Animal Models to Humans.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2015 Jul;35(7):1551-3. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.115.305547. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2015. PMID: 26109737 No abstract available.
References
-
- Murray CJ, Lopez AD. Global mortality, disability, and the contribution of risk factors: Global Burden of Disease Study. Lancet. 1997;349:1436–42. - PubMed
-
- Gordon DJ, Probstfield JL, Garrison RJ, Neaton JD, Castelli WP, Knoke JD, Jacobs DR, Jr, Bangdiwala S, Tyroler HA. High-density lipoprotein cholesterol and cardiovascular disease. Four prospective American studies. Circulation. 1989;79:8–15. - PubMed
-
- Assmann G, Schulte H. Relation of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and triglycerides to incidence of atherosclerotic coronary artery disease (the PROCAM experience). Prospective Cardiovascular Munster study. Am J Cardiol. 1992;70:733–7. - PubMed
-
- McNeish J, Aiello RJ, Guyot D, Turi T, Gabel C, Aldinger C, Hoppe KL, Roach ML, Royer LJ, de Wet J, Broccardo C, Chimini G, Francone OL. High density lipoprotein deficiency and foam cell accumulation in mice with targeted disruption of ATP-binding cassette transporter-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000;97:4245–50. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Timmins JM, Lee JY, Boudyguina E, Kluckman KD, Brunham LR, Mulya A, Gebre AK, Coutinho JM, Colvin PL, Smith TL, Hayden MR, Maeda N, Parks JS. Targeted inactivation of hepatic Abca1 causes profound hypoalphalipoproteinemia and kidney hypercatabolism of apoA-I. J Clin Invest. 2005;115:1333–42. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

