Pharmacophore modeling, in silico screening, molecular docking and molecular dynamics approaches for potential alpha-delta bungarotoxin-4 inhibitors discovery
- PMID: 26109766
- PMCID: PMC4461960
- DOI: 10.4103/0973-1296.157670
Pharmacophore modeling, in silico screening, molecular docking and molecular dynamics approaches for potential alpha-delta bungarotoxin-4 inhibitors discovery
Abstract
Background: The alpha-delta bungartoxin-4 (α-δ-Bgt-4) is a potent neurotoxin produced by highly venomous snake species, Bungarus caeruleus, mainly targeting neuronal acetylcholine receptors (nAchRs) and producing adverse biological malfunctions leading to respiratory paralysis and mortality.
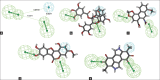
Objective: In this study, we predicted the three-dimensional structure of α-δ-Bgt-4 using homology modeling and investigated the conformational changes and the key residues responsible for nAchRs inhibiting activity.
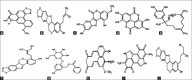
Materials and methods: From the selected plants, which are traditionally used for snake bites, the active compounds are taken and performed molecular interaction studies and also used for modern techniques like pharmacophore modeling and mapping and absorption, distribution, metabolism, elimination and toxicity analysis which may increase the possibility of success.
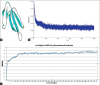
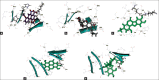
Results: Moreover, 100's of drug-like compounds were retrieved and analyzed through computational virtual screening and allowed for pharmacokinetic profiling, molecular docking and dynamics simulation.
Conclusion: Finally the top five drug-like compounds having competing level of inhibition toward α-δ-Bgt-4 toxin were suggested based on their interaction with α-δ-Bgt-4 toxin.
Keywords: Acetylcholine receptor; bungarotoxin; molecular docking; molecular dynamics; pharmacophore; venom.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Pharmacoinformatic Approach to Explore the Antidote Potential of Phytochemicals on Bungarotoxin from Indian Krait, Bungarus caeruleus.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2018 Oct 31;16:450-461. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2018.10.005. eCollection 2018. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2018. PMID: 30455855 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular modeling and structural analysis of nAChR variants uncovers the mechanism of resistance to snake toxins.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2017 Jun;35(8):1654-1671. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2016.1190791. Epub 2016 Jul 15. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2017. PMID: 27421773
-
Structural insights into pharmacophore-assisted in silico identification of protein-protein interaction inhibitors for inhibition of human toll-like receptor 4 - myeloid differentiation factor-2 (hTLR4-MD-2) complex.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2019 May;37(8):1968-1991. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2018.1474804. Epub 2018 May 29. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2019. PMID: 29842849
-
Natural compounds interacting with nicotinic acetylcholine receptors: from low-molecular weight ones to peptides and proteins.Toxins (Basel). 2015 May 14;7(5):1683-701. doi: 10.3390/toxins7051683. Toxins (Basel). 2015. PMID: 26008231 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Binding of native kappa-neurotoxins and site-directed mutants to nicotinic acetylcholine receptors.Toxicon. 1996 Nov-Dec;34(11-12):1243-56. doi: 10.1016/s0041-0101(96)00110-9. Toxicon. 1996. PMID: 9027980 Review.
Cited by
-
Insights of Endocytosis Signaling in Health and Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 3;24(3):2971. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032971. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36769293 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacoinformatic Approach to Explore the Antidote Potential of Phytochemicals on Bungarotoxin from Indian Krait, Bungarus caeruleus.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2018 Oct 31;16:450-461. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2018.10.005. eCollection 2018. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2018. PMID: 30455855 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berg DK, Conroy WG. Nicotinic alpha 7 receptors: Synaptic options and downstream signaling in neurons. J Neurobiol. 2002;53:512–23. - PubMed
-
- Graham AJ, Martin-Ruiz CM, Teaktong T, Ray MA, Court JA. Molecular cloning, functional properties, and distribution of rat brain alpha 7: A nicotinic cation channel highly permeable to calcium. Curr Drug Target CNS Neurol Disord. 2002;1:387–97.
-
- Bourin M, Ripoll N, Dailly E. Nicotinic receptors and Alzheimer's disease. Curr Med Res Opin. 2003;19:169–77. - PubMed
-
- Banerjee C, Nyengaard JR, Wevers A, de Vos RA, Jansen Steur EN, Lindstrom J, et al. Cellular expression of alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor protein in the temporal cortex in Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease – A stereological approach. Neurobiol Dis. 2000;7:666–72. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
