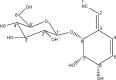
Antibiotic-modifying activity of riachin, a non-cyanogenic cyanoglycoside extracted from Bauhinia pentandra
- PMID: 26109849
- PMCID: PMC4474397
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S84676
Antibiotic-modifying activity of riachin, a non-cyanogenic cyanoglycoside extracted from Bauhinia pentandra
Abstract
Background: The search for new active compounds from the Brazilian flora has intensified in recent years, especially for new drugs with antibiotic potential. Accordingly, the aim of this study was to determine whether riachin has antibiotic activity in itself or is able to modulate the activity of conventional antibiotics.
Methods: A non-cyanogenic cyanoglycoside known as riachin was isolated from Bauhinia pentandra, and was tested alone and in combination with three antibiotics (clindamycin, amikacin, and gentamicin) against multiresistant bacterial strains (Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Staphylococcus aureus).
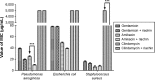
Results: Riachin did not show significant antibiotic activity when tested alone against any strain (P>0.05). However, when combined with conventional antibiotics, it showed drug-modifying activity against strains of S. aureus exposed to clindamycin (P<0.001) as well as against P. aeruginosa exposed to amikacin (P<0.001). Although riachin did not show direct antibiotic activity, it had synergistic activity when combined with amikacin or clindamycin. The mechanism of action of this synergism is under investigation.
Conclusion: The results of this work demonstrate that some substances of natural origin can enhance the effectiveness of certain antibiotics, which means a substantial reduction in the drug dose required and possibly in consequent adverse events for patients.
Keywords: Escherichia coli; Pseudomonas aeruginosa; Staphylococcus aureus; riachin.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Vanillin selectively modulates the action of antibiotics against resistant bacteria.Microb Pathog. 2017 Dec;113:265-268. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2017.10.052. Epub 2017 Oct 28. Microb Pathog. 2017. PMID: 29107747
-
Phytocompounds and modulatory effects of Anacardium microcarpum (cajui) on antibiotic drugs used in clinical infections.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015 Nov 6;9:5965-72. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S93145. eCollection 2015. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015. PMID: 26604695 Free PMC article.
-
Antibacterial sesquiterpene lactone glucoside from seed pods of Bauhinia retusa.J Asian Nat Prod Res. 2011 Jan;13(1):75-9. doi: 10.1080/10286020.2010.543130. J Asian Nat Prod Res. 2011. PMID: 21253953
-
Chemical composition and evaluation of modulatory of the antibiotic activity from extract and essential oil of Myracrodruon urundeuva.Pharm Biol. 2014 May;52(5):560-5. doi: 10.3109/13880209.2013.853810. Epub 2013 Nov 20. Pharm Biol. 2014. PMID: 24251788
-
Phenolic compounds and interaction between aminoglycosides and natural products of Lygodium venustum SW against multiresistant bacteria.Chemotherapy. 2012;58(5):337-40. doi: 10.1159/000343044. Epub 2012 Nov 16. Chemotherapy. 2012. PMID: 23171666
References
-
- Silva NCC, Junior AF. Biological properties of medicinal plants: a review of their antimicrobial activity. J Venom Anim Toxins Incl Trop Dis. 2010;16:402–413.
-
- Nascimento GG, Locatelli J, Freitas PC, Silva GL. Antibacterial activity of plant extracts and phytochemicals on antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Braz J Microbiol. 2000;31:247–256.
-
- Sakagami Y, Kajimura K. Bactericidal activities of disinfectants against vancomycin-resistant enterococci. J Hosp Infect. 2002;50:140–144. - PubMed
-
- Chartone-Souza E. Bactérias ultra-resistentes: uma guerra quase perdida. [Ultra-resistant bacteria: an almost lost war] Cienc Hoje. 1998;23:27–35. Portuguese.
-
- Tintino SR, Guedes GMM, da Cunha FAB, et al. Avaliação in vitro da atividade antimicrobiana e moduladora dos extratos etanólico e hexânico de bulbo de Costus arabicus. [In vitro evaluation of antimicrobial activity and modulating the ethanol and hexane extracts of Costus arabicus bulb] Bioscience Journal. 2013;29:732–738. Portuguese.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

