Diabetes research in Middle East countries; a scientometrics study from 1990 to 2012
- PMID: 26109972
- PMCID: PMC4468230
Diabetes research in Middle East countries; a scientometrics study from 1990 to 2012
Abstract
Background: Diabetes burden is a serious warning for urgent action plan across the world. Knowledge production in this context could provide evidences for more efficient interventions. Aimed to that, we quantify the trend of diabetes research outputs of Middle East countries focusing on the scientific publication numbers, citations, and international collaboration.
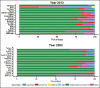
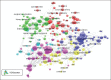
Materials and methods: This scientometrics study was performed based on the systematic analysis through three international databases; ISI, PubMed, and Scopus from 1990 to 2012. International collaboration of Middle East countries and citations was analyzed based on Scopus. Diabetes' publications in Iran specifically were assessed, and frequent used terms were mapped by VOSviewer software.
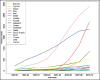
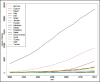
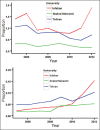
Results: Over 23-year period, the number of diabetes publications and related citations in Middle East countries had increasing trend. The number of articles on diabetes in ISI, PubMed, and Scopus were respectively; 13,994, 11,336, and 20,707. Turkey, Israel, Iran, Saudi Arabia, and Egypt have devoted the five top competition positions. In addition, Israel, Turkey, and Iran were leading countries in citation analysis. The most collaborative country with Middle East countries was USA and within the region, the most collaborative country was Saudi Arabia. Iran in all databases stands on third position and produced 12.7% of diabetes publications within region. Regarding diabetes researches, the frequent used terms in Iranian articles were "effect," "woman," and "metabolic syndrome."
Conclusion: Ascending trend of diabetes research outputs in Middle East countries is appreciated but encouraging to strategic planning for maintaining this trend, and more collaboration between researchers is needed to regional health promotion.
Keywords: Diabetes; Middle East; scientometrics.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Gray M, Schubert L. Sustainable social work: Modelling knowledge production, transfer, and evidence-based practice. Int J Soc Welfare. 2012;21:203–14.
-
- von Krogh G, Nonaka I, Rechsteiner L. Leadership in organizational knowledge creation: A review and framework. J Manage Stud. 2012;49:240–77.
-
- Serenko A, Bontis N, Booker L, Sadeddin K, Hardie T. A scientometric analysis of knowledge management and intellectual capital academic literature (1994-2008) J Knowl Manage. 2010;14:3–23.
-
- Adams J, King Ch, Pendlebury D, Hook D, Wilsdon J. Research Report Middle East Exploring The Changing Landscape of Arabian, Persian and Turkish Research: Thomson Reuters. 2011. [Last accessed on 2014 Apr 25]. Available from: http://www.tumj.ir/pdf/globalresearchreport.pdf .

