Visual vs Fully Automatic Histogram-Based Assessment of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF) Progression Using Sequential Multidetector Computed Tomography (MDCT)
- PMID: 26110421
- PMCID: PMC4482435
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0130653
Visual vs Fully Automatic Histogram-Based Assessment of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF) Progression Using Sequential Multidetector Computed Tomography (MDCT)
Abstract
Objectives: To describe changes over time in extent of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) at multidetector computed tomography (MDCT) assessed by semi-quantitative visual scores (VSs) and fully automatic histogram-based quantitative evaluation and to test the relationship between these two methods of quantification.
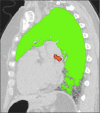
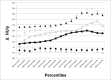
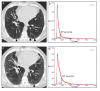
Methods: Forty IPF patients (median age: 70 y, interquartile: 62-75 years; M:F, 33:7) that underwent 2 MDCT at different time points with a median interval of 13 months (interquartile: 10-17 months) were retrospectively evaluated. In-house software YACTA quantified automatically lung density histogram (10th-90th percentile in 5th percentile steps). Longitudinal changes in VSs and in the percentiles of attenuation histogram were obtained in 20 untreated patients and 20 patients treated with pirfenidone. Pearson correlation analysis was used to test the relationship between VSs and selected percentiles.
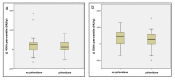
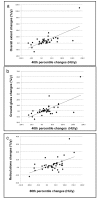
Results: In follow-up MDCT, visual overall extent of parenchymal abnormalities (OE) increased in median by 5%/year (interquartile: 0%/y; +11%/y). Substantial difference was found between treated and untreated patients in HU changes of the 40th and of the 80th percentiles of density histogram. Correlation analysis between VSs and selected percentiles showed higher correlation between the changes (Δ) in OE and Δ 40th percentile (r=0.69; p<0.001) as compared to Δ 80th percentile (r=0.58; p<0.001); closer correlation was found between Δ ground-glass extent and Δ 40th percentile (r=0.66, p<0.001) as compared to Δ 80th percentile (r=0.47, p=0.002), while the Δ reticulations correlated better with the Δ 80th percentile (r=0.56, p<0.001) in comparison to Δ 40th percentile (r=0.43, p=0.003).
Conclusions: There is a relevant and fully automatically measurable difference at MDCT in VSs and in histogram analysis at one year follow-up of IPF patients, whether treated or untreated: Δ 40th percentile might reflect the change in overall extent of lung abnormalities, notably of ground-glass pattern; furthermore Δ 80th percentile might reveal the course of reticular opacities.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Fully Automated Segmentation of Pulmonary Fibrosis Using Different Software Tools.Respiration. 2021;100(7):580-587. doi: 10.1159/000515182. Epub 2021 Apr 15. Respiration. 2021. PMID: 33857945
-
CT analysis of the effect of pirfenidone in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Eur J Radiol. 2014 Jan;83(1):32-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2012.02.014. Epub 2012 Mar 31. Eur J Radiol. 2014. PMID: 22465123 Clinical Trial.
-
CT quantification of the heterogeneity of fibrosis boundaries in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Eur Radiol. 2021 Jul;31(7):5148-5159. doi: 10.1007/s00330-020-07594-y. Epub 2021 Jan 13. Eur Radiol. 2021. PMID: 33439318 Free PMC article.
-
Computer-based quantitative computed tomography image analysis in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A mini review.Respir Investig. 2018 Jan;56(1):5-13. doi: 10.1016/j.resinv.2017.10.003. Epub 2017 Dec 7. Respir Investig. 2018. PMID: 29325682 Review.
-
Pirfenidone: significant treatment effects in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Clin Respir J. 2012 Jul;6(3):131-43. doi: 10.1111/j.1752-699X.2012.00302.x. Clin Respir J. 2012. PMID: 22697264 Review.
Cited by
-
Third-generation CD19.CAR-T cell-containing combination therapy in Scl70+ systemic sclerosis.Ann Rheum Dis. 2024 Mar 12;83(4):543-546. doi: 10.1136/ard-2023-225174. Ann Rheum Dis. 2024. PMID: 38135464 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Normal Lung Quantification in Usual Interstitial Pneumonia Pattern: The Impact of Threshold-based Volumetric CT Analysis for the Staging of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis.PLoS One. 2016 Mar 31;11(3):e0152505. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0152505. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27031615 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of slice-reduced computed tomography on histogram-based densitometry assessment of lung fibrosis in patients with systemic sclerosis.J Thorac Dis. 2018 Apr;10(4):2142-2152. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2018.04.39. J Thorac Dis. 2018. PMID: 29850118 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Comorbidities on Mortality in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis.PLoS One. 2016 Mar 29;11(3):e0151425. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0151425. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27023440 Free PMC article.
-
Computer-Aided Evaluation of Interstitial Lung Diseases.Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 Apr 7;15(7):943. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15070943. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40218293 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

