Reduced Toxicity of Shiga Toxin (Stx) Type 2c in Mice Compared to Stx2d Is Associated with Instability of Stx2c Holotoxin
- PMID: 26110507
- PMCID: PMC4488704
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins7062306
Reduced Toxicity of Shiga Toxin (Stx) Type 2c in Mice Compared to Stx2d Is Associated with Instability of Stx2c Holotoxin
Abstract
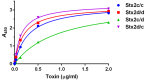
Shiga toxin (Stx) is an AB5 ribotoxin made by Stx-producing Escherichia coli (STEC). These organisms cause diarrhea, hemorrhagic colitis and the hemolytic uremic syndrome. STEC make two types of Stxs, Stx1 and/or Stx2. Stx2 has one prototype (a) and six subtypes (b-g), but only STEC that make Stx2a, and/or Stx2c, or Stx2d are associated with severe disease. However, Stx2c is about 10-fold less toxic than Stx2d in vivo despite only two amino acid differences in the A subunit at positions 291 and 297. We made mutations at these two sites to create intermediate toxins between Stx2c and Stx2d, and determined the 50% cytotoxic dose on Vero cells before and after heat treatment, and the 50% lethal dose in mice of the toxins. We found that serine 291 was associated with increased toxicity in vivo and that either amino acid change from that in Stx2c to that in Stx2d increased heat stability. We also assessed the secondary structure of Stx2c and Stx2d by circular dichroism (CD) spectroscopy. The CD studies suggest that Stx2c has a less-ordered secondary structure than Stx2d. We conclude that both amino acids at positions 291 and 297 in Stx2c contribute to its decreased stability and in vivo toxicity compared to Stx2d.
Keywords: STEC; Shiga toxin; Stx2; Stx2c; Stx2d.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Switching Shiga Toxin (Stx) Type from Stx2d to Stx2a but Not Stx2c Alters Virulence of Stx-Producing Escherichia coli (STEC) Strain B2F1 in Streptomycin (Str)-Treated Mice.Toxins (Basel). 2021 Jan 15;13(1):64. doi: 10.3390/toxins13010064. Toxins (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33467588 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of Shiga toxin type 2d (Stx2d) by elastase involves cleavage of the C-terminal two amino acids of the A2 peptide in the context of the appropriate B pentamer.Mol Microbiol. 2002 Jan;43(1):207-15. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2002.02733.x. Mol Microbiol. 2002. PMID: 11849548
-
Stx2 subtyping of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli isolated from cattle in France: detection of a new Stx2 subtype and correlation with additional virulence factors.J Clin Microbiol. 2001 Sep;39(9):3060-5. doi: 10.1128/JCM.39.9.3060-3065.2001. J Clin Microbiol. 2001. PMID: 11526129 Free PMC article.
-
New aspects in the pathogenesis of enteropathic hemolytic uremic syndrome.Semin Thromb Hemost. 2006 Mar;32(2):105-12. doi: 10.1055/s-2006-939766. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2006. PMID: 16575685 Review.
-
Do the A subunits contribute to the differences in the toxicity of Shiga toxin 1 and Shiga toxin 2?Toxins (Basel). 2015 Apr 29;7(5):1467-85. doi: 10.3390/toxins7051467. Toxins (Basel). 2015. PMID: 25938272 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Bimodal Response to Shiga Toxin 2 Subtypes Results from Relatively Weak Binding to the Target Cell.Infect Immun. 2019 Nov 18;87(12):e00428-19. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00428-19. Print 2019 Dec. Infect Immun. 2019. PMID: 31527121 Free PMC article.
-
Switching Shiga Toxin (Stx) Type from Stx2d to Stx2a but Not Stx2c Alters Virulence of Stx-Producing Escherichia coli (STEC) Strain B2F1 in Streptomycin (Str)-Treated Mice.Toxins (Basel). 2021 Jan 15;13(1):64. doi: 10.3390/toxins13010064. Toxins (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33467588 Free PMC article.
-
Epidemiology of Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli O157 in the Province of Alberta, Canada, 2009-2016.Toxins (Basel). 2019 Oct 22;11(10):613. doi: 10.3390/toxins11100613. Toxins (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31652648 Free PMC article.
-
The Virulence of Escherichia coli O157:H7 Isolates in Mice Depends on Shiga Toxin Type 2a (Stx2a)-Induction and High Levels of Stx2a in Stool.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020 Feb 26;10:62. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.00062. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32175286 Free PMC article.
-
Affinity-Based Screening of Tetravalent Peptides Identifies Subtype-Selective Neutralizers of Shiga Toxin 2d, a Highly Virulent Subtype, by Targeting a Unique Amino Acid Involved in Its Receptor Recognition.Infect Immun. 2016 Aug 19;84(9):2653-61. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00149-16. Print 2016 Sep. Infect Immun. 2016. PMID: 27382021 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

