Hypoxia, AMPK activation and uterine artery vasoreactivity
- PMID: 26110512
- PMCID: PMC4771787
- DOI: 10.1113/JP270995
Hypoxia, AMPK activation and uterine artery vasoreactivity
Abstract
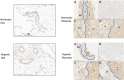
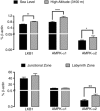
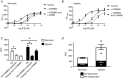
Genes near adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase-α1 (PRKAA1) have been implicated in the greater uterine artery (UtA) blood flow and relative protection from fetal growth restriction seen in altitude-adapted Andean populations. Adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) activation vasodilates multiple vessels but whether AMPK is present in UtA or placental tissue and influences UtA vasoreactivity during normal or hypoxic pregnancy remains unknown. We studied isolated UtA and placenta from near-term C57BL/6J mice housed in normoxia (n = 8) or hypoxia (10% oxygen, n = 7-9) from day 14 to day 19, and placentas from non-labouring sea level (n = 3) or 3100 m (n = 3) women. Hypoxia increased AMPK immunostaining in near-term murine UtA and placental tissue. RT-PCR products for AMPK-α1 and -α2 isoforms and liver kinase B1 (LKB1; the upstream kinase activating AMPK) were present in murine and human placenta, and hypoxia increased LKB1 and AMPK-α1 and -α2 expression in the high- compared with low-altitude human placentas. Pharmacological AMPK activation by A769662 caused phenylephrine pre-constricted UtA from normoxic or hypoxic pregnant mice to dilate and this dilatation was partially reversed by the NOS inhibitor l-NAME. Hypoxic pregnancy sufficient to restrict fetal growth markedly augmented the UtA vasodilator effect of AMPK activation in opposition to PE constriction as the result of both NO-dependent and NO-independent mechanisms. We conclude that AMPK is activated during hypoxic pregnancy and that AMPK activation vasodilates the UtA, especially in hypoxic pregnancy. AMPK activation may be playing an adaptive role by limiting cellular energy depletion and helping to maintain utero-placental blood flow in hypoxic pregnancy.
© 2015 The Authors. The Journal of Physiology © 2015 The Physiological Society.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Maternal AMPK pathway activation with uterine artery blood flow and fetal growth maintenance during hypoxia.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2024 Oct 1;327(4):H778-H792. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00193.2024. Epub 2024 Jul 19. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2024. PMID: 39028630
-
AMP-activated protein kinase activator AICAR attenuates hypoxia-induced murine fetal growth restriction in part by improving uterine artery blood flow.J Physiol. 2020 Sep;598(18):4093-4105. doi: 10.1113/JP279341. Epub 2020 Jul 6. J Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32592403 Free PMC article.
-
AMPK function in uterine vasculature and placenta at high altitude.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2025 Aug 21;380(1933):20240174. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2024.0174. Epub 2025 Aug 21. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40836813 Review.
-
Increased uterine artery blood flow in hypoxic murine pregnancy is not sufficient to prevent fetal growth restriction†.Biol Reprod. 2020 Mar 13;102(3):660-670. doi: 10.1093/biolre/ioz208. Biol Reprod. 2020. PMID: 31711123 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of the LKB1-AMPK Signalling Pathway Underpins Hypoxic Pulmonary Vasoconstriction and Pulmonary Hypertension.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2015;860:89-99. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-18440-1_11. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2015. PMID: 26303471 Review.
Cited by
-
AMP-Activated Protein (AMPK) in Pathophysiology of Pregnancy Complications.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Oct 9;19(10):3076. doi: 10.3390/ijms19103076. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30304773 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypoxia and Placental Development.Birth Defects Res. 2017 Oct 16;109(17):1309-1329. doi: 10.1002/bdr2.1135. Birth Defects Res. 2017. PMID: 29105383 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Placental adaptations supporting fetal growth during normal and adverse gestational environments.Exp Physiol. 2023 Mar;108(3):371-397. doi: 10.1113/EP090442. Epub 2022 Dec 9. Exp Physiol. 2023. PMID: 36484327 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Placental structure, function, and mitochondrial phenotype relate to fetal size in each fetal sex in mice†.Biol Reprod. 2022 Jun 13;106(6):1292-1311. doi: 10.1093/biolre/ioac056. Biol Reprod. 2022. PMID: 35293971 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of hypoxia on uteroplacental and fetoplacental vascular function during pregnancy.Front Physiol. 2024 Dec 18;15:1490154. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2024.1490154. eCollection 2024. Front Physiol. 2024. PMID: 39744703 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Barcroft J (1933). The conditions of fetal respiration. Lancet 222, 1021–1024.
-
- Barron DH, Metcalfe J, Meschia G, Huckabee W, Hellegers A & Prystowsky H (1964). Adaptations of pregnant ewes and their fetuses to high altitude In The Physiological Effects of High Altitude, ed. Weihe WH, pp. 115–129. Macmillan, New York.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

