AtRTD - a comprehensive reference transcript dataset resource for accurate quantification of transcript-specific expression in Arabidopsis thaliana
- PMID: 26111100
- PMCID: PMC4744958
- DOI: 10.1111/nph.13545
AtRTD - a comprehensive reference transcript dataset resource for accurate quantification of transcript-specific expression in Arabidopsis thaliana
Abstract
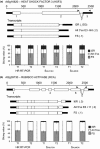
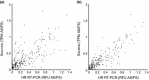
RNA-sequencing (RNA-seq) allows global gene expression analysis at the individual transcript level. Accurate quantification of transcript variants generated by alternative splicing (AS) remains a challenge. We have developed a comprehensive, nonredundant Arabidopsis reference transcript dataset (AtRTD) containing over 74 000 transcripts for use with algorithms to quantify AS transcript isoforms in RNA-seq. The AtRTD was formed by merging transcripts from TAIR10 and novel transcripts identified in an AS discovery project. We have estimated transcript abundance in RNA-seq data using the transcriptome-based alignment-free programmes Sailfish and Salmon and have validated quantification of splicing ratios from RNA-seq by high resolution reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (HR RT-PCR). Good correlations between splicing ratios from RNA-seq and HR RT-PCR were obtained demonstrating the accuracy of abundances calculated for individual transcripts in RNA-seq. The AtRTD is a resource that will have immediate utility in analysing Arabidopsis RNA-seq data to quantify differential transcript abundance and expression.
Keywords: Arabidopsis thaliana; RNA-sequencing (RNA-seq); Sailfish; Salmon; alternative splicing; high resolution reverse transcription (HR RT)-PCR; transcripts per million.
© 2015 The Authors. New Phytologist © 2015 New Phytologist Trust.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A high quality Arabidopsis transcriptome for accurate transcript-level analysis of alternative splicing.Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 May 19;45(9):5061-5073. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx267. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017. PMID: 28402429 Free PMC article.
-
A high-resolution single-molecule sequencing-based Arabidopsis transcriptome using novel methods of Iso-seq analysis.Genome Biol. 2022 Jul 7;23(1):149. doi: 10.1186/s13059-022-02711-0. Genome Biol. 2022. PMID: 35799267 Free PMC article.
-
BaRTv1.0: an improved barley reference transcript dataset to determine accurate changes in the barley transcriptome using RNA-seq.BMC Genomics. 2019 Dec 11;20(1):968. doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-6243-7. BMC Genomics. 2019. PMID: 31829136 Free PMC article.
-
High-quality reference transcript datasets hold the key to transcript-specific RNA-sequencing analysis in plants.New Phytol. 2017 Jan;213(2):525-530. doi: 10.1111/nph.14208. Epub 2016 Sep 23. New Phytol. 2017. PMID: 27659901 Review.
-
Decoding co-/post-transcriptional complexities of plant transcriptomes and epitranscriptome using next-generation sequencing technologies.Biochem Soc Trans. 2020 Dec 18;48(6):2399-2414. doi: 10.1042/BST20190492. Biochem Soc Trans. 2020. PMID: 33196096 Review.
Cited by
-
The cyclin-dependent kinase G group defines a thermo-sensitive alternative splicing circuit modulating the expression of Arabidopsis ATU2AF65A.Plant J. 2018 Jun;94(6):1010-1022. doi: 10.1111/tpj.13914. Epub 2018 May 10. Plant J. 2018. PMID: 29602264 Free PMC article.
-
A high quality Arabidopsis transcriptome for accurate transcript-level analysis of alternative splicing.Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 May 19;45(9):5061-5073. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx267. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017. PMID: 28402429 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated multi-omics framework of the plant response to jasmonic acid.Nat Plants. 2020 Mar;6(3):290-302. doi: 10.1038/s41477-020-0605-7. Epub 2020 Mar 13. Nat Plants. 2020. PMID: 32170290 Free PMC article.
-
Evolutionarily Conserved Alternative Splicing Across Monocots.Genetics. 2017 Oct;207(2):465-480. doi: 10.1534/genetics.117.300189. Epub 2017 Aug 24. Genetics. 2017. PMID: 28839042 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Identification of Splicing Quantitative Trait Loci (sQTLs) in Diverse Ecotypes of Arabidopsis thaliana.Front Plant Sci. 2019 Oct 3;10:1160. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2019.01160. eCollection 2019. Front Plant Sci. 2019. PMID: 31632417 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Airoldi CA, Davies B. 2012. Gene duplication and the evolution of plant MADS‐box transcription factors. Journal of Genetics and Genomics 39: 157–165. - PubMed
-
- Alamancos GP, Pagès A, Trincado JL, Bellora N, Eyras E. 2015. Leveraging transcript quantification for fast computation of alternative splicing profiles. bioRxiv. doi: 10.1101/008763. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bardou F, Ariel F, Simpson CG, Romero‐Barrios N, Laporte P, Balzerque S, Brown JW, Crespi M. 2014. Long noncoding RNA modulates alternative splicing regulators in Arabidopsis . Developmental Cell 30: 166–176. - PubMed
-
- Black DL. 2003. Mechanisms of alternative pre‐messenger RNA splicing. Annual Review of Biochemistry 72: 291–336. - PubMed
-
- Carvalho RF, Feijão CV, Duque P. 2013. On the physiological significance of alternative splicing events in higher plants. Protoplasma 250: 639–650. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

