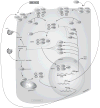
PharmGKB summary: peginterferon-α pathway
- PMID: 26111151
- PMCID: PMC4757589
- DOI: 10.1097/FPC.0000000000000158
PharmGKB summary: peginterferon-α pathway
Conflict of interest statement
R.B.A. and T.E.K. are stockholders in Personalis Inc. For the remaining authors, there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Foster GR. Pegylated interferons for the treatment of chronic hepatitis C: pharmacological and clinical differences between peginterferon-alpha-2a and peginterferon-alpha-2b. Drugs. 2010;70:147–165. - PubMed
-
- [Accessed 28 April 2015];Hepatitis C WHO fact sheet. Available at: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs164/en/
-
- Hoofnagle JH. Course and outcome of hepatitis C. Hepatology. 2002;36:S21–S29. - PubMed
-
- Hoofnagle JH, Seeff LB. Peginterferon and ribavirin for chronic hepatitis C. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:2444–2451. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources