Epigenetic modifications of caveolae associated proteins in health and disease
- PMID: 26112043
- PMCID: PMC4482180
- DOI: 10.1186/s12863-015-0231-y
Epigenetic modifications of caveolae associated proteins in health and disease
Abstract
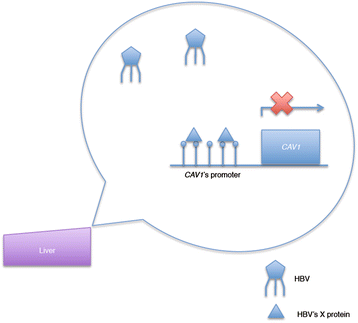
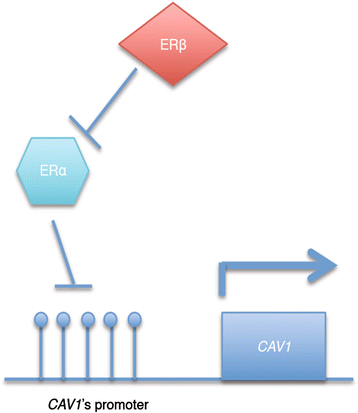
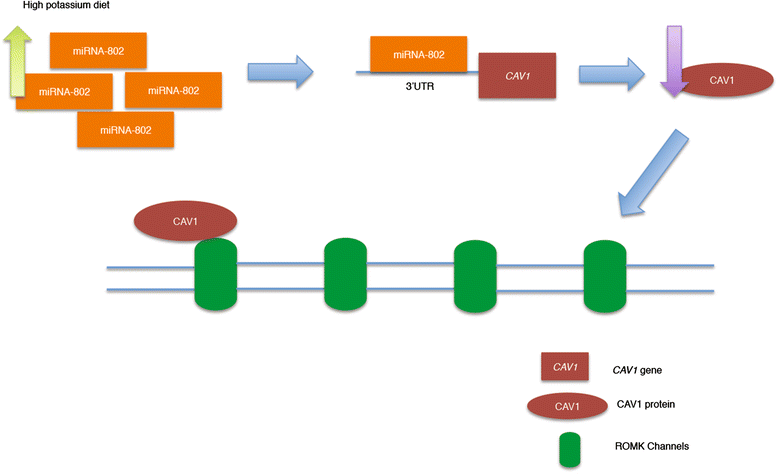
Caveolae are small, "omega-shaped" invaginations at the plasma membrane of the cell which are involved in a variety of processes including cholesterol transport, potocytosis and cell signalling. Within caveolae there are caveolae-associated proteins, and changes in expression of these molecules have been described to play a role in the pathophysiology of various diseases including cancer and cardiovascular disease. Evidence is beginning to accumulate that epigenetic processes may regulate the expression of these caveolae related genes, and hence contribute to disease progression. Here, we summarize the current knowledge of the role of epigenetic modification in regulating the expression of these caveolae related genes and how this relates to changes in cellular physiology and in health and disease.
Figures
References
-
- Parton RG, Simons K. The multiple faces of caveolae. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8(3):185–94. - PubMed
-
- Parton RG, del Pozo MA. Caveolae as plasma membrane sensors, protectors and organizers. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2013;14(2):98–112. - PubMed
-
- Glenney JR., Jr The sequence of human caveolin reveals identity with VIP21, a component of transport vesicles. FEBS Lett. 1992;314(1):45–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

