Identification and characterization of a HEPN-MNT family type II toxin-antitoxin in Shewanella oneidensis
- PMID: 26112399
- PMCID: PMC4621449
- DOI: 10.1111/1751-7915.12294
Identification and characterization of a HEPN-MNT family type II toxin-antitoxin in Shewanella oneidensis
Abstract
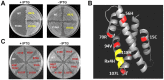
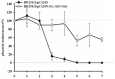
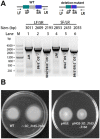
Toxin-antitoxin (TA) systems are prevalent in bacteria and archaea. However, related studies in the ecologically and bioelectrochemically important strain Shewanella oneidensis are limited. Here, we show that SO_3166, a member of the higher eukaryotes and prokaryotes nucleotide-binding (HEPN) superfamily, strongly inhibited cell growth in S. oneidensis and Escherichia coli. SO_3165, a putative minimal nucleotidyltransferase (MNT), neutralized the toxicity of SO_3166. Gene SO_3165 lies upstream of SO_3166, and they are co-transcribed. Moreover, the SO_3165 and SO_3166 proteins interact with each other directly in vivo, and antitoxin SO_3165 bound to the promoter of the TA operon and repressed its activity. Finally, the conserved Rx4-6H domain in HEPN family was identified in SO_3166. Mutating either the R or H abolished SO_3166 toxicity, confirming that Rx4-6H domain is critical for SO_3166 activity. Taken together, these results demonstrate that SO_3166 and SO_3165 in S. oneidensis form a typical type II TA pair. This TA pair plays a critical role in regulating bacterial functions because its disruption led to impaired cell motility in S. oneidensis. Thus, we demonstrated for the first time that HEPN-MNT can function as a TA system, thereby providing important insights into the understanding of the function and regulation of HEPNs and MNTs in prokaryotes.
© 2015 The Authors. Microbial Biotechnology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd and Society for Applied Microbiology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Structure-function analyses reveal the molecular architecture and neutralization mechanism of a bacterial HEPN-MNT toxin-antitoxin system.J Biol Chem. 2018 May 4;293(18):6812-6823. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.002421. Epub 2018 Mar 19. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29555683 Free PMC article.
-
Novel polyadenylylation-dependent neutralization mechanism of the HEPN/MNT toxin/antitoxin system.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 Nov 4;48(19):11054-11067. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa855. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 33045733 Free PMC article.
-
Type II toxin/antitoxin system ParESO /CopASO stabilizes prophage CP4So in Shewanella oneidensis.Environ Microbiol. 2018 Mar;20(3):1224-1239. doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.14068. Epub 2018 Mar 25. Environ Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29411516
-
Regulation of toxin-antitoxin systems by proteolysis.Plasmid. 2013 Jul;70(1):33-41. doi: 10.1016/j.plasmid.2013.01.007. Epub 2013 Feb 8. Plasmid. 2013. PMID: 23396045 Review.
-
Toxin-antitoxin systems in bacteria and archaea.Annu Rev Genet. 2011;45:61-79. doi: 10.1146/annurev-genet-110410-132412. Annu Rev Genet. 2011. PMID: 22060041 Review.
Cited by
-
Focused Overview of Mycobacterium tuberculosis VapBC Toxin-Antitoxin Systems Regarding Their Structural and Functional Aspects: Including Insights on Biomimetic Peptides.Biomimetics (Basel). 2023 Sep 6;8(5):412. doi: 10.3390/biomimetics8050412. Biomimetics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37754163 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification and Characterization of HEPN-MNT Type II TA System from Methanothermobacter thermautotrophicus ΔH.J Microbiol. 2023 Apr;61(4):411-421. doi: 10.1007/s12275-023-00041-9. Epub 2023 Apr 18. J Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37071293
-
Structural insight into the distinct regulatory mechanism of the HEPN-MNT toxin-antitoxin system in Legionella pneumophila.Nat Commun. 2024 Nov 24;15(1):10188. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-54551-0. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39582057 Free PMC article.
-
Mobile Genetic Elements and Evolution of CRISPR-Cas Systems: All the Way There and Back.Genome Biol Evol. 2017 Oct 1;9(10):2812-2825. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evx192. Genome Biol Evol. 2017. PMID: 28985291 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of the Deep-Sea Streptomyces sp. SCSIO 02999 Derived VapC/VapB Toxin-Antitoxin System in Escherichia coli.Toxins (Basel). 2016 Jul 1;8(7):195. doi: 10.3390/toxins8070195. Toxins (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27376329 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Belitsky M, Avshalom H, Erental A, Yelin I, Kumar S, London N, et al. The Escherichia coli Extracellular Death Factor EDF induces the endoribonucleolytic activities of the toxins MazF and ChpBK. Mol Cell. 2011;41:625–635. - PubMed
-
- Bernard P. Couturier M. Cell killing by the F plasmid CcdB protein involves poisoning of DNA-topoisomerase II complexes. J Mol Biol. 1992;226:735–745. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

